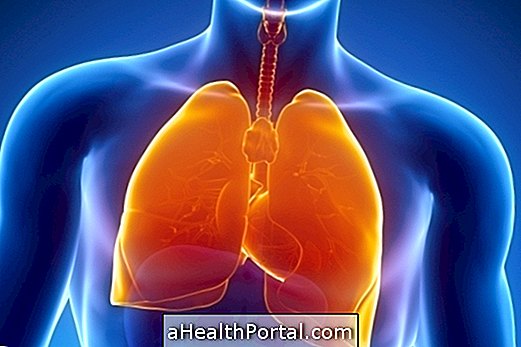
Bilateral pneumonia is a situation in which there is infection and inflammation of both lungs by microorganisms and, therefore, it is considered more serious than common pneumonia, because it is associated with decreased respiratory capacity. As a result, there is a decrease in the amount of oxygen circulating in the body, including in the brain, which can lead to changes in the person's level of consciousness.
This type of pneumonia is more common in people with weakened immune systems, such as babies, older people or people who have chronic illnesses that can interfere with the functioning of the immune system.
The causes of bilateral pneumonia are the same as those of common pneumonia, and can be caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi, however, as the symptoms are more severe, treatment is usually done in a hospital environment so that the person is monitored and receives oxygen , so it is possible to reduce the risk of complications such as generalized infection, respiratory arrest or pleural effusion, for example.
Main symptoms
The symptoms of bilateral pneumonia are mainly related to the person's breathing capacity, which can be quite compromised, since both lungs are compromised. The main symptoms of bilateral pneumonia are:
- Fever higher than 38ºC;
- Cough with a lot of phlegm;
- Great difficulty in breathing;
- Increased respiratory rate;
- Easy and intense tiredness.
When the person has other symptoms related to the lack of oxygen, such as slightly bluish lips or altered levels of consciousness, it is very important to inform the pulmonologist so that the treatment can be done as soon as possible, especially with the use of oxygen masks. . Know how to recognize the symptoms of pneumonia.
How the treatment is done
The treatment for bilateral pneumonia should be guided by the pulmonologist, being defined by means of a system that classifies patients according to the symptoms described and the results of the exams. Patients classified as low risk are usually treated at home with the use of antibiotics, such as Levofloxacin or Clarithromycin, for example, the time of use being defined by the doctor.
In addition, it is important that the person remains at rest during treatment, drink plenty of fluids, spray with drinking water and avoid public spaces or with a lot of pollution, in addition to wearing protective masks whenever necessary.
In the case of patients classified as severe, especially when the patient is elderly or has impaired renal function, blood pressure and great difficulty in performing gas exchanges, treatment is carried out in a hospital environment. Treatment at the hospital usually lasts between 1 and 2 weeks, and may vary according to the patient's response to therapy, and is usually done by administering oxygen and antibiotics. After discharge, antibiotic treatment should be continued for at least 1 week or according to the pulmonologist's recommendation.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther















.jpg)
