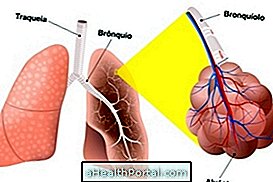
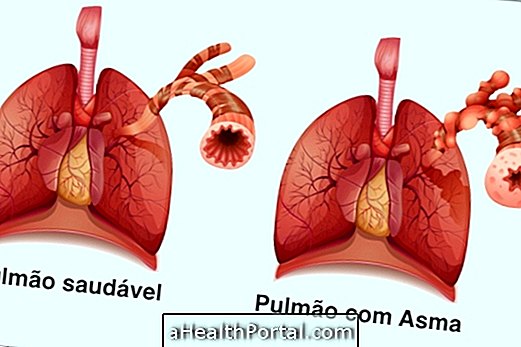
Tracheobronchitis is an inflammation of the trachea and bronchi that causes symptoms such as coughing hoarseness and difficulty breathing because of excess mucus, which causes the bronchi to become narrower, making it difficult for the respiratory system to function.
Tracheobronchitis usually arises after an infection in the respiratory tract, such as the flu, rhinitis, or sinusitis, but it can also be caused by an allergic reaction to animal hair or cigarette smoke, for example, being similar to asthma in these cases.
Tracheobronchitis is cured, and treatment is usually given for 15 days with bronchodilator drugs and antibiotics to help decrease symptoms.

Symptoms of tracheobronchitis
The main symptoms of tracheobronchitis include:
- Dry or secreted cough;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Constant wheezing when breathing;
- Fever above 38 ° C;
- Chest pain.
When these symptoms occur, it is recommended to go to the emergency room or consult a pulmonologist to diagnose the problem and initiate appropriate treatment.
See a more complete list of tracheobronchitis signs in: Tracheobronchitis Symptoms.
Treatment for tracheobronchitis
The treatment for tracheobronchitis should be guided by a pulmonologist and is usually started with the use of cough medicines such as levodropropizine and mucolytic remedies such as carbocysteine, which eliminate excess secretions from the lung to facilitate breathing.
In addition, if tracheobronchitis is being caused by an infection, your doctor may also prescribe the use of an antibiotic, such as Clindamycin or Lincomycin, to fight bacteria and speed up treatment.
In the most severe cases, treatment of tracheobronchitis should be done at hospital admission to make medicine directly into the vein and receive oxygen. Usually, the patient is discharged about 5 days after hospitalization and should maintain treatment at home.
Home treatment
A good home remedy for the relief of tracheobronchitis symptoms is to take the mauve or guaco tea as a way of supplementing antibiotic treatment.
Malva tea
This tea is good because mauve is a natural anti-inflammatory that dilates the bronchi. However, it should not be used in high doses because it may become laxative.
Ingredients
- 5 grams of leaves and dried mauve flowers
- 1 liter of water
Method of preparation
Boil the leaves and mauve flowers for 5 minutes. Strain the mixture and drink 1 to 3 cups a day.
Guaco tea
Guaco tea helps in the treatment of tracheobronchitis, reducing the amount of sputum. The guaco besides bronchodilator is a natural expectorant because it relaxes the musculature of the airways.
Ingredients
- 3 grams of dried guaco leaves
- 150 ml of water
Method of preparation
Place the guaco leaves in boiling water for 10 minutes. Allow to cool for 15 minutes and strain. Drink 2 cups of tea per day. Honey can be added to sweeten the beverage and taken hot overnight.
How to prevent tracheobronchitis
Because a virus can be transmitted from one person to another easily, the best way to prevent acute tracheobronchitis is not to stay indoors for too long, to avoid crowding and to sanitize properly, thereby diseases.








.png)


