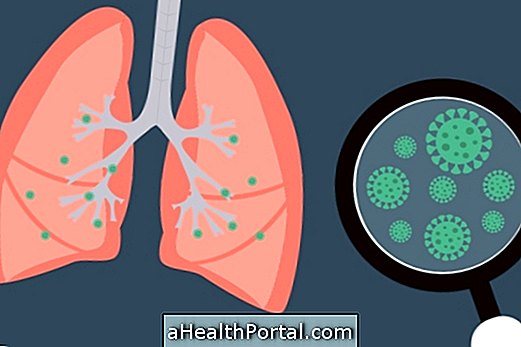
Childhood pneumonia is an infection in the child's lung, which produces flu-like symptoms but worsens over the course of days and can be difficult to identify.
Generally, childhood pneumonia is caused by viruses or bacteria that mainly affect babies under 1 year of age, and therefore, children should be dressed appropriately to avoid sudden changes in temperature and avoid smoking near them, especially in the home because cigarette smoke is a common cause of diseases like the tire monia in children.
Childhood pneumonia is curable and rarely contagious, and should be treated at home with rest, fever medicines, antibiotics, and ingestion of fluids such as water and milk.

Symptoms and Diagnosis
The main signs and symptoms of childhood pneumonia include:
- Fever above 38º;
- Cough with catarrh;
- Lack of appetite;
- Breathing faster and shorter, with opening of the nostrils;
- Effort to breathe with a lot of movement of the ribs;
- Easy fatigue, not wanting to play.
Babies and children with these symptoms should be evaluated by a pediatrician as soon as possible to start treatment within the first 48 hours and avoid serious complications such as respiratory arrest. In the case of the baby, when he has a fever above 39 °, refuses to eat, vomiting or diarrhea, he must be taken to the hospital, as he may need to be hospitalized. A serious type of pneumonia is SARS, so check out its symptoms.
Know the remedies used and when the treatment should be done in the hospital by clicking here.
The pediatrician may arrive at the diagnosis of pneumonia after observing the symptoms and requesting a chest x-ray to evaluate the presence of secretions and regions that are not receiving air in the lungs. Increased respiratory rate in infants usually indicates pneumonia and is sufficient to reach this diagnosis when there is:
- Babies up to 2 months old: 60 or more inspirations per minute;
- Babies from 2 months to 1 year: 50 or more inspirations per minute;
- Children 1 to 5 years: 40 or more inspirations per minute.
The baby's or infant's breathing rate should be checked when it is quiet and calm, such as during sleep, for example.
Babies with more risk of pneumonia
Babies who are at greatest risk of developing pneumonia are those born with less than 2kg; in case of malnutrition; when they were not breastfed and also those who are most exposed to cigarette smoke, when there is nearby smoke due to wood or manure. In addition, infants and children who do not get measles, whooping cough vaccines are also more likely to have pneumonia.

Types of pneumonia in children
The types of pneumonia are classified according to their cause. Consideration is given to the type of microorganism involved, the location where the child was contaminated, and how this contamination occurred. The types of pneumonia are:
- Bacterial pneumonia: it is an infection caused by bacteria and the treatment can be done with antibiotics;
- Viral pneumonia: it is caused by viruses and treatment is more prolonged because there are no antiviral drugs for all existing viruses;
- Aspiration pneumonia: it arises after aspirating a liquid, like its own vomit, and can be caused by both viruses and bacteria;
- Atypical pneumonia: it is caused by microorganisms different from those of common pneumonia, such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae;
- Community pneumonia: is a serious lung infection that gets caught outside the hospital or within the first 48 hours of hospital admission?
- Hospital pneumonia: when pneumonia develops while the individual is hospitalized or up to 72 hours after discharge.
Pneumonia is a contagious disease but it is not common for a child to pass pneumonia on to others. The most common type of pneumonia in children is viral, which occurs after a worsening flu.
How To Treat Childhood Pneumonia
The treatment for childhood pneumonia lasts about 2 weeks and can be done at home with oral antibiotics such as Amoxicillin or Azithromycin, which depend on the child's weight.
In addition, some childhood pneumonia care that helps with treatment include:
- Make nebulisations as directed by your doctor.
- Maintain good nutrition with fruits;
- Offer enough milk and water;
- Maintain rest and avoid public spaces, such as day care or school;
- Dress the child according to the season of the year;
- Avoid drafts during and after bathing.
Hospital admission is reserved for more severe cases where it is necessary to have physiotherapy for childhood pneumonia, to receive oxygen or to make antibiotics in the vein.
Symptom improvement occurs around the 2nd day of treatment, but the pediatrician must have a chest x-ray and a physical examination to confirm the cure for pneumonia.












-o-que--causas-e-tratamento.jpg)




