A cough with blood, technically called hemoptysis, is not always a sign of a serious problem and may only come from a small wound in the nose or throat that bleeds when you cough.
However, if the cough is accompanied by bright red blood it can also be a sign of more serious health problems such as pneumonia, tuberculosis or lung cancer, especially when it happens for more than a day.
Thus, it is recommended to consult the general practitioner or a pulmonologist whenever the cough with blood takes more than 24 hours to disappear or when the amount of blood is large or increases over time.

1. Injuries to the airways
In most cases, blood cough is caused by simple nose injuries, throat irritation, or due to some tests such as bronchoscopy, lung biopsy, endoscopy, or surgery to remove tonsils.
What to do: in most cases, the cough with blood goes away on its own without needing any treatment, however, if it stays for more than 1 day it is important to go to the pulmonologist to identify the problem and start the appropriate treatment.
2. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that usually causes symptoms such as coughing up blood, sudden fever and above 38 ° C, shortness of breath and chest pain. It usually arises after a cold or ill-treated cold, where viruses or bacteria can reach the alveoli, damaging the arrival of oxygen in the cells. Diagnosis is based on tests and treatment may include antibiotics.
What to do: Since some types of pneumonia need to be treated with antibiotics it is advised to go to the pulmonologist to confirm the diagnosis and start the appropriate treatment. In more severe cases, pneumonia can greatly affect breathing, and may even require hospitalization. Learn more about the treatment of this infection and what options are available.
3. Tuberculosis
In addition to the cough with blood, very characteristic of cases of tuberculosis, this disease can also cause other signs like constant fever, night sweats, excessive tiredness and weight loss. In this case the cough must be present for more than 3 weeks and does not seem to be related to any flu. The examination that identifies pulmonary tuberculosis is the examination of the sputum and the treatment is done with antibiotics.
What to do: Tuberculosis is caused by a bacterium and therefore its treatment is always done with antibiotics that need to be used for several months until the infection completely heals. Thus, whenever there is suspicion of tuberculosis it is very important to consult a pulmonologist. In addition, if the diagnosis is confirmed, the nearest people should be advised to also be tested for tuberculosis, as the disease spreads easily. See more details of treatment.
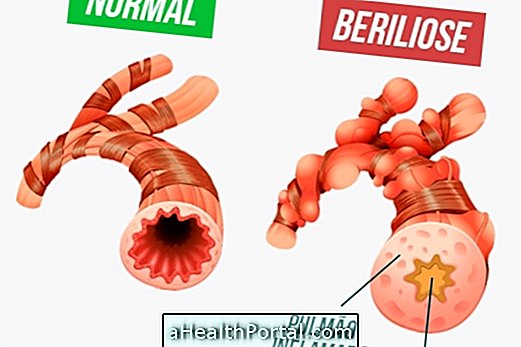
4. Bronchiectasis
This respiratory disease causes coughing up of blood that worsens gradually due to permanent dilation of the bronchi, which can be caused by a bacterial infection or by other respiratory diseases such as bronchitis, asthma or pneumonia.
What to do: in most cases bronchiectasis has no cure, however, it is possible to use drugs that help relieve symptoms greatly, improving the quality of life. These remedies may be prescribed by a pulmonologist after evaluation of the symptoms. Learn more about this disease and what treatment options.
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a serious problem that should be treated as soon as possible in the hospital. It usually happens due to the presence of a clot that prevents the passage of blood to the lung, causing death of the affected tissues and intense difficulty to breathe. Thus, in addition to coughing up blood, it is very common to feel extreme shortness of breath, bluish fingers, chest pain and increased heart rate. Understand more about how pulmonary embolism develops.
What to do: whenever there is an intense shortness of breath accompanied by chest pain and cough it is very important to go to the hospital quickly to confirm if it is not a serious problem such as a heart attack or pulmonary embolism.
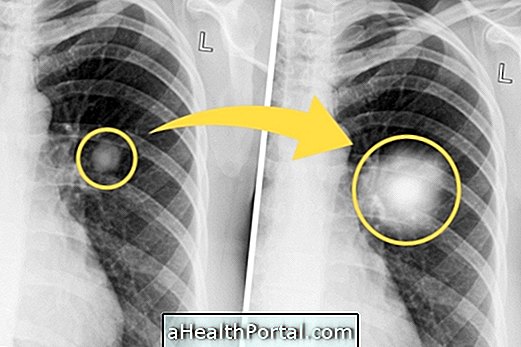
6. Lung cancer
There is suspicion of lung cancer when there is a cough with blood and weight loss in the last few months without diet or exercise. Other symptoms that may be present are fatigue and weakness, which can occur when the cancer starts in the lung, as it is most common in people who smoke, or when there are metastases in the lung. Learn about other symptoms that may indicate lung cancer.
What to do: The success of cancer treatment is always greater the earlier the cancer is diagnosed. Therefore, whenever there are symptoms that may indicate a lung problem, it is very important to consult a pulmonologist. In addition, people with a family history of lung cancer or those who smoke should make recurrent consultations with the pulmonologist, especially after age 50.

When to go to the doctor
When observing the presence of cough with blood one must remain calm and try to find its cause. Some situations that must be observed are:
- Amount of blood present;
- If there is blood in the mouth or nose;
- When blood was first observed;
- If the person has already presented any respiratory illness before this symptom arises;
- If there are other symptoms such as shortness of breath, shortness of breath, shortness of breath, shortness of breath, fever, headache or fainting.
If you suspect that the situation is serious, you should call 192 and call the SAMU or go to the emergency room for the situation to be evaluated by a doctor.
What can be coughing up blood in babies
In children the most common cause is the presence of small objects that they put in the nose or mouth and end up going to the lungs causing dry cough and vestiges of blood. In this case it is common not to have much blood involved but it is important to take the child to the hospital to have an x-ray removed in order to identify the cause.
The doctor may also use a small instrument to look at the child's ears, nose, and throat for small objects such as earrings, tarrachas, corn, peas, beans, or toys that may have been introduced there. Depending on the object inserted and its location, it can be removed with forceps and in the most severe cases surgery may even be necessary.
Other, less common causes of coughing up blood in infants and children are lung or heart disease, which should be diagnosed and treated by the pediatrician. If in doubt, consult your pediatrician.