Pneumopathies correspond to diseases in which there is involvement of the lungs due to the presence of microorganisms or substances foreign to the body, for example, leading to the onset of cough, fever and shortness of breath.
The treatment of pneumopathy is done according to the cause, and can be done with the use of antibiotics, antiparasitics or steroid medicines according to the medical recommendation.
Types of pneumopathy
Pneumopathies can be classified into several types according to their cause in:
- Interstitial pneumonitis, in which there is involvement of the deepest region of the lung, the interstitial tissue. Examples of interstitial pneumopathies are alveolitis and pulmonary fibrosis. Understand lung fibrosis and how the treatment is done;
- Infectious pneumonia, the cause of which is pneumopathy caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites, such as Ascaris lumbricoides, Taenia solium and Ancylostoma sp ., Since during their infectious cycle they can leave the intestine and, through the bloodstream, in the lungs, leading to the involvement of this organ, being then called parasitic pneumopathy. The main example of pneumopathy caused by an infectious agent is pneumonia, which corresponds to the involvement of the lungs mainly by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae . Know the symptoms of pneumonia;
- Chronic pneumonopathy, which is the type of pneumopathy whose symptoms last longer than 3 months even with the correct treatment, not having cure in some cases, such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or COPD. See what it is and how to identify COPD;
- Occupational pneumonopathy, which corresponds to lung involvement due to work situations, may occur when the worker does not respect the safety measures related to the performance of the activity. Work-related pneumopathy is called Pneumoconiosis. Learn about the types of pneumoconiosis and how to avoid them.
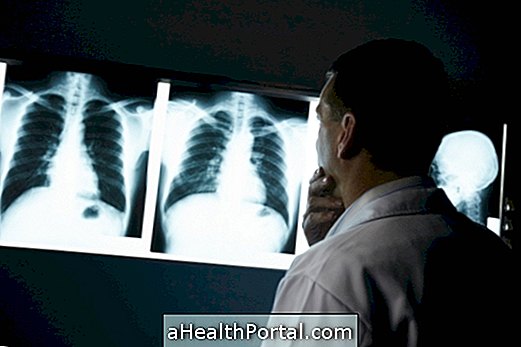
The diagnosis of pneumopathies can be made by a general practitioner or pulmonologist by evaluating the symptoms and outcome of the chest X-ray, where areas where the lung is compromised can be observed.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of pneumopathy vary depending on the cause, but usually include high fever, cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and increased heart rate.
It is important that your doctor assess your symptoms so you can be aware of the severity and thus establish the best treatment.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment for pneumopathy varies according to the lung disease that the individual presents, but it can be done through the use of antibiotic, antifungal or antiparasitic medicines, in the case of infectious pneumopathy, for example. The use of corticosteroids may also be recommended to relieve symptoms and decrease inflammation of the lungs. All medicines should be used in accordance with medical advice.
In more severe cases of pneumopathies, the hospitalization of the person may be necessary in addition to oxygen therapy.