Obesity is characterized by overweight, usually caused by sedentary lifestyle and overconsumption of foods rich in fat and sugar, which generates various maladies in a person's life, such as the development of diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, cholesterol elevated, infarct or osteoarthritis of the bones, as well as symptoms such as difficulties in exertion, indisposition and low self-esteem.
To identify that a person is obese, most of the time, the BMI, or body mass index, is a calculation that analyzes the weight that the person presents in relation to his height, being divided in different degrees:
- Normal weight : BMI between 18.0 and 24.9 kg / m2
- Overweight : BMI between 25.0 and 29.9 kg / m2
- Grade 1 obesity: BMI between 30.0 - 34.9 kg / m2;
- Obesity grade 2: BMI between 35.0 - 39.9 kg / m2;
- Obesity grade 3 or morbid obesity: BMI equal to or greater than 40 kg / m2.
You can also use our calculator to find the IMC:

Types of obesity
In addition to being classified according to weight, obesity also varies according to the location and distribution of fat by the body:
1. Abdominal obesity

The fat is deposited mainly in the abdomen and the waist, and it can also be distributed through the chest and face. This type of obesity is also known as android or apple-shaped obesity due to the similarity of silhouette of the person with this fruit, and is more common in men, although some women may also have.
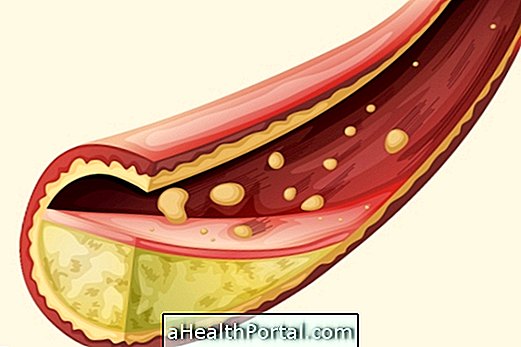
Abdominal obesity is very associated with great risk for developing other cardiovascular diseases like high cholesterol, heart disease, heart attack, plus diabetes, inflammation and thrombosis.
2. Peripheral obesity

This type of obesity is more common in women because the fat is located more in the thighs, hips and buttocks, and is known as pear obesity due to the shape of the silhouette, or obesity gynoid.
Peripheral obesity is more associated with circulatory problems such as venous insufficiency and varicose veins, and osteoarthritis in the knees due to the overload of weight in these joints, although it also increases the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
3. Homogeneous obesity
In this case, there is no predominance of fat in a localized area, as excess weight is distributed throughout the body. This can be dangerous because a person can be careless because there is not a great impact on physical appearance, as in other types.
Signs and symptoms of obesity
Excess fat has negative effects on the whole body, causing uncomfortable signs and symptoms, such as:
- Shortness of breath and breathing difficulties due to abdominal pressure on the lungs;
- Pain in the body, especially in the back, legs, knees and shoulders, due to the excess effort that the body makes to support the weight;
- Difficulty to make efforts or walks, due to the excess weight and deconditioning of the body;
- Dermatitis and fungal infections, due to the accumulation of sweat and dirt in the folds of the body;
- Dark spots on the skin, especially the neck, armpits and groins, a reaction caused by insulin resistance, or pre-diabetes, called acanthosis nigricans ;
- Impotence and infertility, due to hormonal changes and difficulties in blood flow in the vessels;
- Nocturnal snoring and sleep apnea, by accumulation of fat in the neck and respiratory tract;
- Greater tendency to varicose veins and venous ulcers, due to changes in vessels and blood circulation;
- Anxiety and depression due to dissatisfaction with body image and binge eating.
In addition, obesity is a determining cause of various diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure, stroke, stroke, thrombosis, and impotence, and metabolic diseases such as diabetes and high cholesterol.
What Causes Obesity
Obesity can occur at any age, and in Brazil, the number of people who go through this situation is increasing due to excessive consumption of caloric foods such as bread, pasta, sweets, fast food and ready meals, as well as sedentary lifestyle, which causes the amount of calories consumed to be greater than the amount that the person spends throughout the day.
In addition, hormonal disorders or emotional problems such as anxiety or nervousness may also increase the risk of obesity and therefore these situations should be addressed as soon as they are identified. Understand better what are the main causes that explain the onset of obesity and how to fight it.
Childhood obesity has also been increasingly frequent, due to the excess of processed foods, sweets and soda, in addition to less and less outdoor activities. The child usually follows the habits of the parents, so it is very common that the children of obese are also overweight.

How to know if I am very overweight
The main way to detect obesity is to calculate BMI, however, in addition to the increased weight, it is also important to identify the fat deposit in different places of the body, differentiating the weight in fat from the weight in muscles.
Thus, as a way to evaluate the mass of fat the body and its distribution, it is used:
- Measurement of skinfold thickness : Measures the fat located in the deposits under the skin, which is related to the amount of internal fat;
- Bioimpedance : An exam that analyzes body composition, indicating the approximate amount of muscles, bones and body fat. Understand better when bioimpedance is indicated and how it works;
- Ultrasonography, tomography or magnetic resonance : assess the thickness of the adipose tissue in the folds, and also in deeper tissues in the different body regions, such as abdomen, therefore, are good methods to evaluate abdominal obesity;
-
Measurement of abdominal circumference : identifies fat deposition in the abdomen and the risk of developing abdominal obesity, being classified as having this type of obesity when the waist measurement exceeds 94 cm in men and 80 cm in women;
- Abdominal / hip circumference ratio : measures the relationship between abdominal and hip circumference, assessing differences in fat accumulation patterns and the risk of developing obesity, being high when above 0.90 for men and 0.85 for women. Learn how you can measure waist-to-hip ratio.
Ideally, these assessments and measurements should be made by the nutritionist or physician, to correctly identify the amount of fat a person needs to eliminate and schedule an optimal treatment.
How to treat obesity
The treatment of obesity should be done with regular physical exercise, guided by a physical trainer, and a nutritionist-oriented diet, and it should be done gradually and healthily, as diets that promise a weight loss very fast, usually do not bring lasting effects or are harmful to health.
Check out some tips to adjust your diet, naturally and healthy, to achieve the goal of weight loss:

Weight-loss medicines can also be used to treat obesity, but their use should only be done under the guidance of the endocrinologist. In more severe cases, one can still resort to some types of surgery such as bariatric surgery. Learn how obesity treatment is done and when medicine or surgery is indicated.