Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi that causes symptoms such as coughing and shortness of breath and their treatment can be done with the use of bronchodilator and expectorant medicines prescribed by the pulmonologist.
Bronchitis is usually known for acute bronchitis, since it lasts less than 3 months, but can also be classified into:
- Asthmatic bronchitis : it is caused by a respiratory allergy and therefore not always curable but can be controlled with the use of medicines prescribed by the doctor and home remedies may also be useful.
- Chronic Bronchitis : Bronchitis is a bronchitis in which symptoms last more than 3 months, even with seemingly appropriate treatment. It can be treated with medications prescribed by the pulmonologist, but physical therapy and the use of natural remedies such as expectorant-effect teas can help release secretions and facilitate breathing. There is a greater chance of cure when there is no chronic obstructive pulmonary disease involved.
- Allergic bronchitis : is closely related to a respiratory allergy and is not contagious. It does not always have a cure, but the use of vaccines may be helpful in controlling the allergic reaction, which may represent a cure for some patients.
Although it is commonly diagnosed in childhood, acute bronchitis can occur at any age and even during pregnancy. See how this disease manifests itself during pregnancy in: Bronchitis in pregnancy.
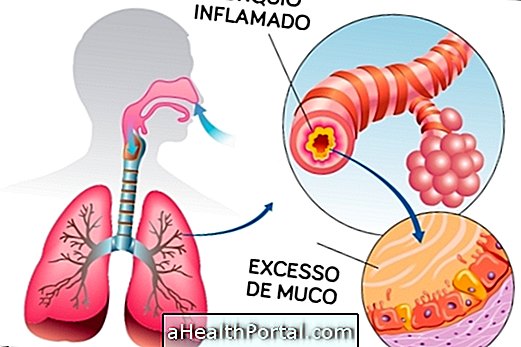
Symptoms of Bronchitis
The signs and symptoms of bronchitis usually include:
- Cough;
- White catarrh, or yellowish if there is infection;
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing;
- Noise when breathing;
- Lips and tips of purplish or bluish fingers;
- Swelling in the legs due to worsening heart work;
- There may be a fever;
- Tiredness;
- Lack of appetite.
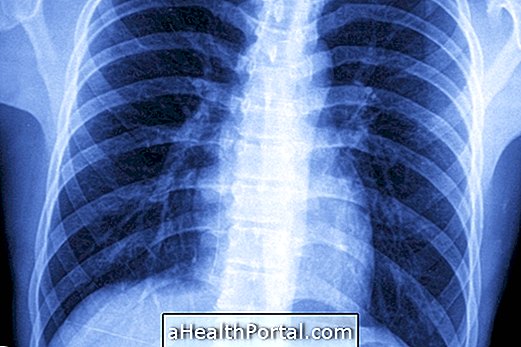
In the persistence of symptoms, it is common for the patient to develop pneumonia and, to diagnose the complication, a chest X-ray is necessary. Learn to identify if it is a Pneumonia Symptom.
Treatment for Bronchitis
The treatment of acute bronchitis can be done with the use of bronchodilator, anti-inflammatory, corticoid, expectorant or mucolytic remedies prescribed by the pulmonologist after the correct diagnosis of the disease.
Some tips that may be useful for the treatment of bronchitis are:
- Rest and drink plenty of liquids, such as water or teas, to fluidize the secretions, facilitating their withdrawal;
- Do physical exercises, such as swimming, to help mobilize and remove secretions, making breathing easier. But care must be taken to be in a pool with little chlorine;
- Conduct physiotherapy sessions to increase the individual's respiratory capacity and eliminate secretions through manual techniques, use of breathing apparatus and breathing exercises.
In addition, the use of medicinal plants with antiseptic and expectorant properties such as Copaíba Oil may also help in the treatment of this problem. See other home remedies and natural remedies that help in home remedy for bronchitis.
Most of the time, bronchitis has a cure. It is only in the elderly, smokers, and individuals with chronic heart or lung disease, such as asthma, that bronchitis can become chronic and can not be cured. However, proper treatment can decrease symptoms and improve the quality of life of the individual.
Causes of Bronchitis
The causes of bronchitis may be related to other diseases, such as chronic sinusitis, allergy, tonsillitis; inhalation of toxic substances, cigarettes or pollutants, or contamination with certain fungi, viruses or bacteria.
The diagnosis of bronchitis can be made after observation of the symptoms that the individual presents and pulmonary auscultation. Tests that may be helpful are: x-ray, sputum examination, and spirometry to assess the extent of bronchitis and thus indicate the best form of treatment.