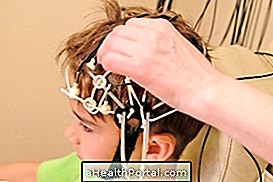
The electroencephalogram (EEG) is a diagnostic test that records the electrical activity of the brain and is used to identify neurological changes, such as seizures or episodes of altered consciousness, for example.
Usually, it is done by attaching small metal plaques on the scalp, called electrodes, which are attached to a computer that records the brain's electrical waves, being a test widely used for not causing pain and being able to be performed by people of any age.
The electroencephalogram can be done either in wakefulness, that is, with the person awake, or during sleep, depending on when the seizures or the problem is being studied, and it may also be necessary to practice maneuvers to activate brain activity, such as breathing exercises or putting a pulsating light in front of the patient.

Price
The electroencephalogram can be performed free of charge by SUS, with medical indication, but it is also performed in private exam clinics, with a price that can vary between 100 and 700 reais, depending on the type of encephalogram and the place of the exam .
What is it for
The electroencephalogram is usually requested by a neurologist and usually serves to identify or diagnose neurological changes, such as:
- Epilepsy;
- Suspected changes in brain activity;
- Cases of altered consciousness, such as fainting or coma, for example;
- Detection of brain inflammation or intoxication;
- Complement of the evaluation of patients with brain diseases, such as dementia, or psychiatric diseases;
- Observe and monitor the treatment of epilepsy;
- Evaluation of brain death. Understand when it happens and how to detect brain death.
However, it is recommended that it be avoided in people with skin lesions on the scalp or pediculosis (lice).

Main types and how it is done
The common electroencephalogram is done by implanting the electrode fixation, with a conductive gel, on areas of the scalp, so that brain activities are captured and recorded through a computer. During the examination, the physician may indicate that maneuvers are performed to activate the brain activity and increase the sensitivity of the examination, such as hyperventilating, rapid breathing, or a pulsating light placed in front of the patient.
In addition, the examination can be done in different ways, such as:
- Waking electroencephalogram : it is the most common type of examination, done with the patient awake, very useful to identify most of the alterations;
- Electroencephalogram in sleep : it is performed during the sleep of the person, who spends the night in the hospital, facilitating the detection of brain changes that may arise during sleep, in cases of sleep apnea, for example;
- Electroencephalogram with cerebral mapping : it is an improvement of the examination, in which the cerebral activity captured by the electrodes is transmitted to a computer, which creates a map capable of making it possible to identify the regions of the brain that are currently active.
To identify and diagnose diseases, your doctor may use imaging tests, such as MRI or CT, which are more sensitive to detect changes such as nodules, tumors, or bleeding. Understand better the indications and how CT and magnetic resonance imaging are done.
How to prepare for the encephalogram
In order to prepare for the encephalogram and to improve its effectiveness in detecting changes, it is necessary to avoid drugs that alter the functioning of the brain, such as sedatives, antiepileptics or antidepressants, 1 to 2 days before the examination or according to the doctor's drink caffeinated beverages such as coffee, tea, or chocolate 12 hours prior to the exam, and avoid using oils, creams or hair sprays on the day of the test.
In addition, if the electroencephalogram is done during sleep, the physician may request that the patient sleep less than 4 to 5 hours the night before to facilitate deep sleep during the examination.