Achalasia is a disease of the esophagus characterized by the absence of peristaltic movements that push food into the stomach and by the narrowing of the esophageal sphincter, which causes difficulty in swallowing solids and liquids, night cough and weight loss, for example.
This disease can happen at any age, however it is more common between the ages of 20 and 40 and has a gradual progression over the years. It is important that achalasia is identified and treated quickly so that complications such as nutritional deficiencies, respiratory problems and even cancer of the esophagus can be avoided.
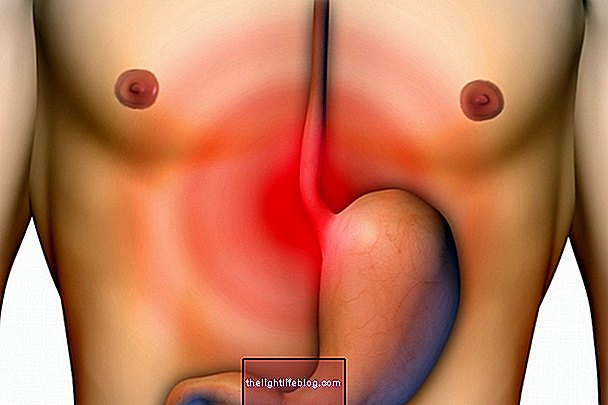
Causes of Achalasia
Achalasia happens due to a change in the nerves that innervate the esophageal muscles, resulting in a decrease or absence of muscle contractions that allow the passage of food.
Achalasia does not yet have a well-established cause, however it is believed that it can happen as a result of autoimmune diseases and viral infections. In addition, cases of achalasia due to Chagas disease due to the wear and tear of the esophageal nerves caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, which is the infectious agent responsible for Chagas disease.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of achalasia are:
- Difficulty swallowing solids and liquids;
- Chest pain;
- Gastric reflux;
- Night cough;
- Airway infections;
- Breathing problems.
In addition, it is possible to notice weight loss due to less food intake and difficulty in emptying the esophagus.
How is the diagnosis
The diagnosis of achalasia is made by the gastroenterologist or general practitioner through the analysis of symptoms and observation of the esophagus through specific exams, such as upper digestive endoscopy, radiography with contrast of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, and esophageal manometry.
In some cases, it may also be necessary to perform a biopsy to check whether the symptoms presented are related to cancer or other diseases. The tests requested are used not only to conclude the diagnosis but also to define the severity of the disease, which is important for the doctor to establish the treatment.
Achalasia Treatment
Achalasia treatment aims to widen the esophagus to allow food to pass properly to the stomach. For this, some techniques are used, such as filling a balloon inside the esophagus to permanently enlarge muscle bundles, and the use of nitroglycerin and calcium blockers before meals, which help to relax the sphincter and decrease symptoms.
The surgery used in this treatment consists of cutting the muscle fibers of the esophagus, and despite the side effects, it has been shown to be the most effective technique in the treatment for achalasia.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- TRINDADE, Eduardo N .; BOZA, Juliana, C .; TRINDADE, Manoel Roberto M. Achalasia Treatment: Dilatation or Surgery?. Brazilian Journal of Videosurgery. Vol 4. 4 ed; 181-182, 2006
- LAURINO-NETO, Rafael M. et al. Diagnostic evaluation of Esophageal Achalasia: from symptoms to Chicago classification. ABCD Arq Bras Cir Dig. Vol 31. 2nd ed; 2018
- MSD MANUAL. Achalasia (Cardiospasm, Esophageal Aperistalsis, Megaesophagus). Available in: . Accessed on 12 Jun 2019


















.jpg)
