Pulmonary emphysema is a serious respiratory disease that usually develops in the lungs of people who have smoked cigarettes for many years. The disease leads to decreased lung elasticity and destruction of the lung alveoli, causing symptoms such as rapid breathing, coughing or difficulty breathing.
Pulmonary emphysema has no cure, but its symptoms can be alleviated, and even avoided, by using some medications and changing some lifestyle habits, which should be indicated by the pulmonologist.

Symptoms of Pulmonary Emphysema
The most common signs and symptoms of pulmonary emphysema include:
- Difficulty breathing;
- Breathing breath;
- Cough;
- Feeling of shortness of breath, with the worsening of the disease.
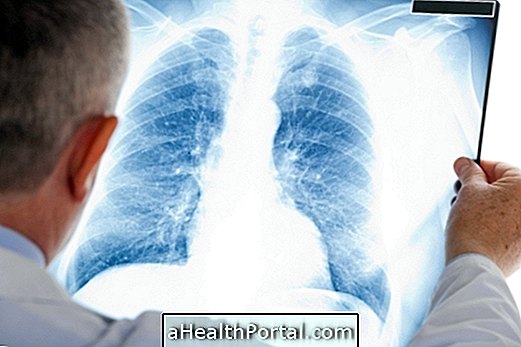
The diagnosis of the disease is based on the symptoms presented and the patient's life history. An examination will be ordered to evaluate lung inflammation and pulmonary auscultation will be performed to check the sounds produced by the lung at the time of breathing. In addition, a test should be done to assess lung capacities, called spirometry, which measures the volume of inspiratory air to check whether or not they are satisfactory beyond x-ray and blood gas analysis.
See other symptoms may indicate pulmonary emphysema.
How does pulmonary emphysema arise?
Emphysema is characterized by the destruction of a large number of alveoli that are small structures within the lung, which are responsible for gas exchange and oxygen entry into the bloodstream. In addition, there is a compromise in lung capacity to expand. Thus, oxygen can not enter properly into the body and the shortness of breath appears because the lungs fill with air but do not empty completely to allow new air to enter.
What Causes Pulmonary Emphysema
About 80% of cases of emphysema occur in smokers, because cigarette smoke affects the lung alveoli, decreasing airflow. But emphysema can also be caused by a deficiency of the enzyme alpha-1 antitrypsin or by other diseases such as chronic bronchitis, asthma or cystic fibrosis, for example.

How is the treatment done?
The treatment of pulmonary emphysema should always be guided by a pulmonologist, since it is necessary to adapt it to the symptoms presented and to the degree of development of the disease. However, in all cases it is important to avoid using cigarettes and do not stay in places with too much pollution or smoke.
In addition, remedies may be prescribed to dilate the lung structures and assist the entry of air, such as Salbutamol or Salmeterol. But in case of more intense symptoms, it may also be necessary to use corticosteroids, such as Beclomethasone or Budesonide, to relieve inflammation of the airways and reduce the difficulty in breathing.
The doctor may also recommend sessions of respiratory physiotherapy, which uses exercises that help to expand the lung and increase the levels of oxygen in the body. Understand the proper treatment of pulmonary emphysema, with medications, surgery, signs of improvement, worsening and possible complications.
Home treatment
A great home treatment to manage emphysema is to breathe properly. For this you should sit on the bed or on the couch with your legs straight and lying down, place your hands on your belly and inhale to watch the movements in the abdomen and chest. When breathing in, you should count up to 2 seconds while the air enters the lungs and to exhale you should press your lips slightly, prolonging the exhalation. To help you remember this strategy try to 'inhale by imagining the smell of a flower and exhale by gently blowing a candle'.
Does pulmonary emphysema turn to cancer?
Emphysema is not cancer, but it increases a person's chances of developing lung cancer, especially if they continue to smoke after diagnosis.
Life time in pulmonary emphysema
Although pulmonary emphysema is a serious respiratory disease, and affects the quality of life of the person, more than 80% of those affected live more than 5 years after the diagnosis of the disease. However, the time varies according to other conditions like age, general health, living habits, and whether the treatment is performed properly.
How to prevent pulmonary emphysema
The best way to prevent emphysema is not to smoke, but not staying in places where there is cigarette smoke is also important. Other ways include treating any respiratory infection as soon as possible, such as flu, cold, bronchitis, and pneumonia. Other tips are:
- Avoid air pollutants, in-house air fresheners, chlorine and other strong-smelling products;
- Avoid strong emotions such as anger, aggression, anxiety and stress;
- Avoid staying in extremes of temperature, both in a very hot place, and in very cold places;
- Avoid staying near fires or grills because of smoke;
- Avoid staying in places with fog, because air quality is lower;
- Take the flu vaccine every year.
In addition, it must have a healthy and balanced diet, preferring vegetables, fruits, whole grains and vegetables, increasingly decreasing consumption of processed, high-salt foods. Taking ginger tea regularly is a good preventative strategy because it is antioxidant and anti-inflammatory and is useful for keeping cells healthy.