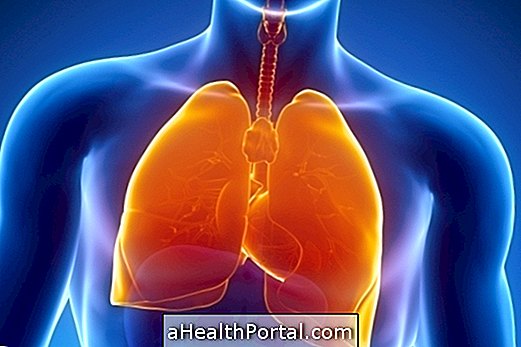
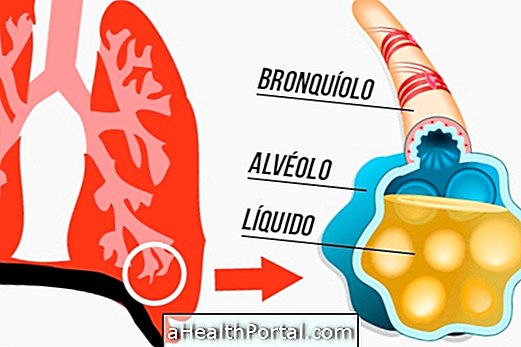
Water in the lung is a health problem known scientifically as pulmonary edema, which occurs when the lung alveoli become filled with fluid due to other diseases not treated properly such as heart failure or respiratory infections, for example.
Since excess fluid in the lungs makes it difficult to breathe and slows down oxygen in the body, water in the lung can be life-threatening and it is therefore advised to go to the emergency room quickly when symptoms appear as too much difficulty. breathing, wheezing or persistent coughing up of blood.
Water in the lung is healing, however, treatment should be started as soon as possible to prevent oxygen levels in the body from falling too high and life-threatening. Understand how water treatment is done in the lung.
Main symptoms
Depending on the cause of the pulmonary edema, the symptoms may appear over time or appear suddenly. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Difficulty breathing, which worsens when lying down;
- Feeling of suffocation or drowning;
- Intense wheezing when breathing;
- Cough with secretion that may contain blood;
- Severe chest pain;
- Tiredness very easy;
- Swelling of the legs or feet.
When more than one of these symptoms occur, it is advisable to call for medical help, call 192, or go to a hospital emergency room immediately to have an X-ray of the chest, confirm the diagnosis, and start treatment promptly. to avoid serious complications that can lead to death.
How to confirm the diagnosis
In most cases, to confirm the diagnosis of pulmonary edema, the physician only observes the symptoms and assesses the history of the person's illness. However, in some cases it may be necessary to have tests such as pulmonary auscultation or chest x-ray to confirm the diagnosis.

What can cause pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema occurs whenever the lungs fill with fluid, making it difficult for air to enter. The most common cases arise when there is a cardiovascular disease, such as coronary heart disease, heart failure or high blood pressure, because the heart can stop working properly, causing a blood accumulation in the lung.
However, there are other situations that can cause the accumulation of liquids such as:
- Adult respiratory distress syndrome;
- Climb to altitudes above 2400 meters, such as climbing a mountain;
- Problems of the nervous system, such as head trauma, subarachnoid haemorrhage or seizure;
- Infections caused by viruses in the lungs;
- Inhalation of smoke;
- Nearly drowning, especially when hearing inhalation of water.
The problem of water in the lung is more frequent in the elderly due to health problems, but it can also happen in children, especially when they are hospitalized and have serum directly in the vein.
Learn more about the possible causes of this problem.
How is the treatment done?
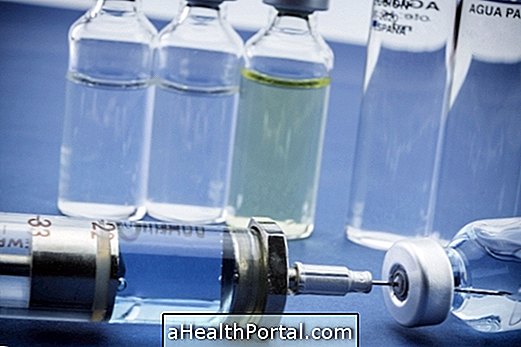
Treatment for water in the lung should be done in hospital inpatient and is usually initiated with the administration of oxygen through a mask to relieve symptoms such as difficulty in breathing, feeling of drowning and wheezing. Thereafter, some remedies may be used to eliminate excess fluid such as:
- Diuretic medicines, such as furosemide: help eliminate excess fluids from the body through the urine;
- Heart medicines, such as nitroglycerin: relieves pressure on the heart arteries, improving their functioning and preventing blood from accumulating in the lungs;
- Morphine : It is used to relieve the feeling of intense lack of air or strong chest pain;
- High blood pressure medicines, such as Captopril: reduce blood pressure, making it easier for the heart to work and preventing fluid buildup.
Due to the effect of the remedies to eliminate excess fluids, the doctor may recommend using a bladder catheter during hospitalization to avoid having to always go to the bathroom to urinate. See how to properly care for the bladder catheter to prevent infection.
In addition to treatment for pulmonary edema, it is very important to find out the cause and start treatment appropriately in order to prevent the problem from recurring.