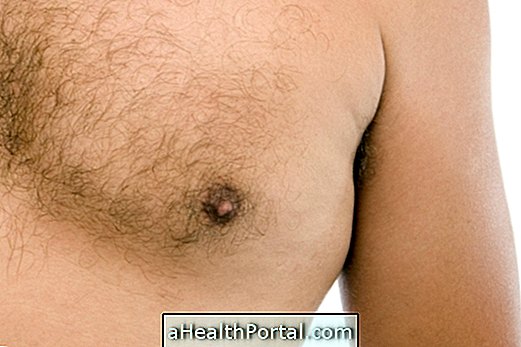
Gynecomastia is a disorder that occurs in man, most often at puberty, which is characterized by enlarged breasts, which can happen due to excess breast glandular tissue, overweight or even diseases.
False gynecomastia occurs in men who are overweight and develop enlargement of the breasts. In this case there are no mammary glands next to the fat and therefore the hormonal medicines are not indicated for the treatment. This type of breast augmentation in man is called lipomastia.
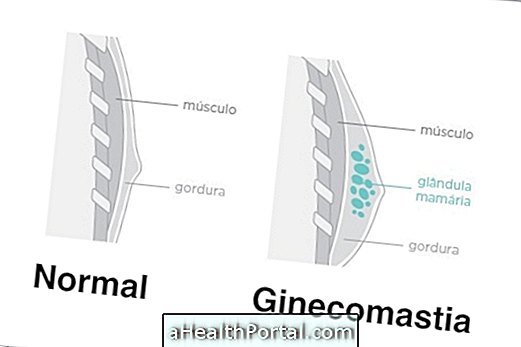
Gynecomastia occurs when there are mammary glands located where there should be only a thin layer of fat and in this case, this can occur in one breast, having the name of unilateral gynecomastia, or in both breasts, being called bilateral gynecomastia. When it occurs in both breasts, they usually increase unevenly, which impairs the boy's self-esteem.
Gynecomastia has a cure because at puberty it is usually transient, disappears spontaneously or can be corrected through treatment with the elimination of its cause or through plastic surgery.
Main causes
The causes of gynecomastia can be changes in male and female hormones, liver diseases, some drug treatments with female hormones, taking anabolic drugs, consuming drugs such as marijuana or testicular or pulmonary tumors, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, pleural effusion or tuberculosis.
The remedies that are proven to lead to breast augmentation in men are estrogen-containing creams or substances such as:
- clomiphene, cannabis, isoniazid,
- gonadotrophin, growth hormone,
- bisulfan, nitrosurea, vincristine,
- ketoconazole, metronidazole,
- etomidate, leuprolide, flutamide,
- finasteride, cyproterone, cimetidine,
- calcium channel blockers, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors,
- beta-blockers, amiodarone, methyldopa, nitrates, neuroleptics,
- diazepam, spironolactone, phenytoin, tricyclic antidepressants,
- haloperidol, amphetamines, theophylline, omeprazole, domperidone, heparin and AIDS medicines.
In cases where gynecomastia is caused by the use of medications, its use should be discontinued, if at all possible.
Types of gynecomastia
Types of gynecomastia include:
- Grade 1 gynecomastia, in which the appearance of a mass of concentrated mammary glandular tissue, such as a button around the areola, does not exist accumulation of skin or fat;
- Grade 2 gynecomastia, where the mass of breast tissue is diffuse, and there may be accumulation of fat;
- Grade 3 gynaecomastia, where the mass of breast tissue is quite diffuse, and there is also excess fat in the place.
Depending on the type of gynecomastia increase in degree, surgery is more complex.
How to identify
To identify gynecomastia, it is sufficient to observe the size and shape of the male breastplate. Breast augmentation is often disruptive and disgraceful to men as it is associated with psychological factors such as embarrassment and limitations in sport and other social activities, such as going to the beach or wearing fairer clothing.
How to treat
Treatment for gynecomastia is related to the cause. When gynecomastia is due to hormonal imbalance, the treatment is done with hormones to regulate them. An example of a remedy for gynecomastia is Tamoxifen, which is an antiestrogen that blocks the effects of estrogens, which are female hormones.
In cases where the remedies had no effect, surgery for gynecomastia is indicated for reduction of the breast or breasts. Here's how the surgery is done: Treatment for gynecomastia.