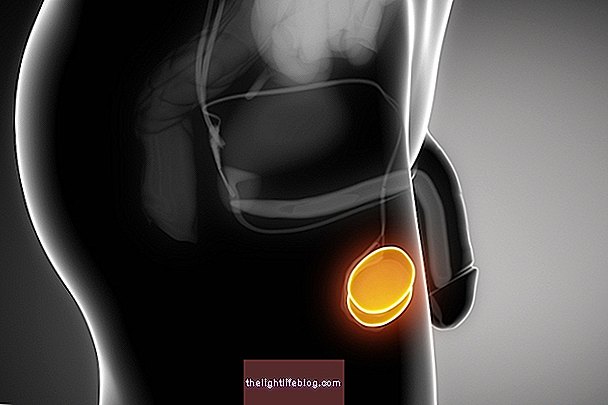
The scrotal hernia is a consequence of the development of the inguinal hernia, which is a bulge that appears in the groin. In the case of the scrotal hernia, the groin protrusion increases and moves to the scrotum, which is the pouch that surrounds and protects the testicles, causing them to swell. Understand how inguinal hernia happens.
This type of hernia can be considered limiting for men, as the scrotum becomes very swollen, causing discomfort and pain. Usually the only treatment option is surgery, but drugs to relieve pain and discomfort as analgesics and anti-inflammatories can also be used.
Main symptoms
The symptoms of scrotal hernia are similar to that of inguinal hernia:
- Protuberance in the groin and scrotum;
- Pain or discomfort when getting up, carrying weight or bowing;
- Feeling of weight;
- Sexual dysfunction.
In the baby, the scrotal hernia can be noticed when changing the baby's diaper, where it can show swelling of the place, or when the baby cries, which can allow the visualization of the protrusion.
If scrotal hernia is not treated, it can lead to intestinal strangulation, where there is no blood flow to the intestine, causing tissue death and symptoms such as vomiting, abdominal distention and absence of stool. In addition, scrotal hernia can lead to infertility, as sperm storage can be compromised. See what are the main causes of infertility.
How is the diagnosis made?
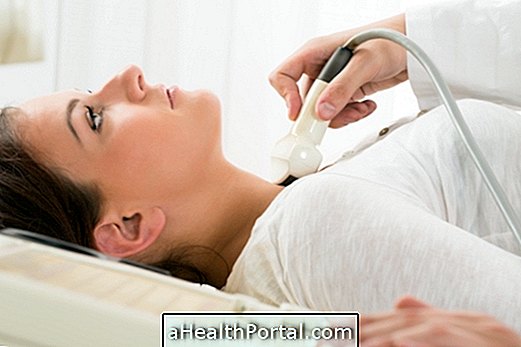
The diagnosis is made from a physical examination performed by the doctor, in which the scrotum and groin are analyzed, as well as the evaluation of the symptoms that the man feels. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may request to perform some imaging examination, such as ultrasonography, for example.
Treatment of scrotal hernia
Treatment of scrotal hernia is usually surgical and should be done as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed to avoid complications such as infertility and intestinal strangulation. The surgery lasts about 2 hours and is done under local or general anesthesia. In some cases the doctor may even put on a kind of net to prevent the hernia from coming back.
In addition, the physician may recommend the use of anti-inflammatory or analgesic drugs, such as ibuprofen and paracetamol, before and after surgery for pain relief, as well as antibiotics after the surgical procedure to prevent the occurrence of infections.
After surgery, it is important for the man to avoid taking too much weight, to sleep on his belly, to increase fiber consumption, not to drive and not to sit for a long time. These post-surgical care are important to keep the hernia from coming back.