Chest pain is not always a symptom of angina or infarction, and may be related to breathing problems, excessive gas, anxiety attacks or muscle fatigue, for example. So the most important thing is to observe when the pain arises, what type it is and if it is accompanied by other symptoms, like fever or nausea.
Pain is usually worrisome when it gets worse when exerting effort, or when it comes with shortness of breath, nausea, or cold sweat, and is usually related to muscle when it hurts when you feel the area. Pinch pains are more frequent in cases of excess gas that cause stitches in the chest, which disappear and reappear. Understand how to differentiate infarction from other types of pain in myocardial infarction symptoms.
As there are many possibilities for a chest pain, it is important to go to the hospital whenever it lasts longer than 20 minutes to decrease or when it worsens over time, especially when other symptoms such as dizziness, cold sweats, trouble breathing, or headache.
We list here the differences between the main causes of chest pain so that it is possible to identify and know what to do each one:

1. Excess gases
This is possibly the most common cause of pain in the chest region and is not related to heart problems, often appearing in people suffering from constipation. The accumulation of gas in the intestine can push some abdominal organs, eventually creating a pain that radiates to the chest.
How to Identify: It is usually a sharp stabbing pain that disappears, but that reappears repeatedly, especially when bending over the belly to pick up something from the floor, for example;
What to do: A good strategy is to massage the bowel to help push the gases, but you can also adopt a position that facilitates the elimination of gases. Here's how:

2. Anxiety and stress
Anxiety, as well as excessive stress, cause an increase in muscle tension in the ribs, as well as an increase in heart rate. This combination causes a chest pain sensation, which can arise even when the person does not feel stressed, happening more commonly in those who are frequently stressed or suffer from panic and anxiety syndrome.
How to identify: It is usually accompanied by other symptoms such as rapid breathing, excessive sweating, rapid heartbeat, nausea, and even changes in bowel function.
What to do : Try to rest in a quiet place, take a soothing tea, like valerian, or do some leisure activity, such as watching a movie, playing games, going to the gym or doing gardening. Here are some more tips on ending anxiety and stress.
3. Muscle pain
Muscle injuries are very common on a daily basis, especially in those who go to the gym or do some kind of sport. However, they can also happen after simpler activities such as coughing or picking up heavy objects. In addition, during stress or fear situations, muscles can also become very contracted, resulting in inflammation and pain.
How to identify : It is a pain that can worsen when breathing, but that is also aggravated when turning the trunk, to look back, for example. In addition to arising after situations as indicated above.
What to do : A good way to relieve muscle pain is to rest and apply warm compresses over the sore area. It can also help lengthen the chest muscles by placing both arms stretched back and grasping the hands. Understand how a muscle strain occurs and what to do to avoid it.

4. Gastroesophageal reflux
People suffering from gastroesophageal reflux and not on an adequate diet are more likely to experience frequent chest pain as it is related to inflammation of the esophagus that occurs when stomach acid reaches the walls of the organ. When this happens, in addition to intense burning, it is also possible to feel chest pain.
How to identify: In most cases it is a pain in the middle of the chest that comes along with burning and stomach pain, however, it can also arise with a slight throat tightening, which happens due to spasms of the esophagus.
What to do: Take a tea of chamomile or ginger as it improves digestion and decreases the acidity of the stomach, reducing inflammation of the esophagus. In addition, one can take an antacid such as Gaviscon, Pepsamar or Eno fruit salt. Out of the crisis should be maintained a light diet, without fatty or spicy foods, for example.
Understand how diet should be for reflux sufferers.
5. Ulcer in the stomach
The pain caused by the presence of an ulcer in the stomach happens due to the inflammation of the walls of the organ and can be easily confused with a pain in the heart, due to the proximity of the two organs.
How to identify: It is a pain located in the middle of the chest, but it can also radiate to the right side, depending on the location of the ulcer. In addition, it is most common after meals and can be accompanied by full stomach feeling, nausea and vomiting.
What to do: One should consult a gastroenterologist when there is suspicion of ulcer in the stomach to start the appropriate treatment with gastric protectors, such as Omeprazole, and avoid complications such as perforation. However, while waiting for the consultation you can alleviate the symptoms with a potato juice. See the recipe.
6. Gallbladder problems
The gallbladder is a small organ that sits on the right side of the stomach and may become inflamed due to the presence of stones or excessive consumption of fat, for example. When this happens, there is a pain in the right side of the chest that can radiate to the heart, looking like a heart attack.
How to identify: It mainly affects the right side of the chest and worsens after eating, especially after eating greasier foods such as fried or sausage. In addition it can also arise with nausea and full stomach feeling.
What to do: Avoid eating fatty foods and drinking plenty of water. Check out some more nutrition tips to stop the pain caused by the gallbladder:

7. Problems in the lungs
Before being a symptom of heart problems, chest pain is more common in changes that happen in the lungs, such as bronchitis, asthma or infection, for example. Because a part of the lung is located in the chest and behind the heart, this pain can be felt to be heart, although it is not.
How to identify: It is a pain that can appear on the right or left side of the chest, but it gets worse when breathing, especially when deep breathing. There may also be a feeling of shortness of breath, wheezing, or frequent coughing.
What to do: a pneumologist should be consulted to identify the specific cause of the pain and initiate appropriate treatment.
8. Heart diseases
Heart disease such as arrhythmia, heart failure, heart muscle inflammation, or coronary heart disease usually does not have chest pain, and other symptoms are more common. Excessive tiredness or palpitations. However, with more intense exercise, these types of problems can cause pain. Here are the 8 possible causes of heart pain.
How to identify: It is a pain that does not appear to be caused by any of the reasons listed above and is accompanied by other symptoms such as changes in heart rate, palpitations, generalized swelling, excessive tiredness and fast breathing, for example. Understand more about the symptoms of heart disease.
What to do: You should consult a cardiologist to do tests for the heart and identify if there is any change that may be causing the pain, starting the appropriate treatment.
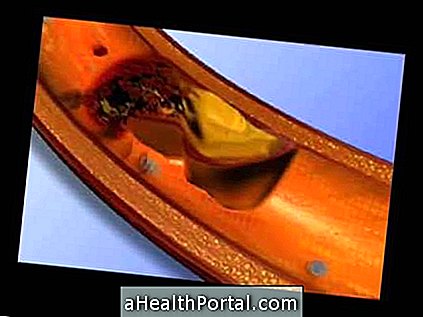
9. Infarction
Infarction, although it is the first concern of those who suffer from chest pain, is usually a rare cause, being more common in people with uncontrolled high blood pressure, very high cholesterol, age greater than 45 years or smokers.
How to identify : It is a pain more localized in the left side of the chest, in the form of a tightening, that does not improve after 20 minutes, being able to radiate to one of the arms, or jaw, causing a sensation of tingling.
What to do : It is recommended that you look for an emergency room to have a heart test, such as an electrocardiogram and chest x-ray, to identify if there is a heart attack, and to start treatment as circulation medicines if necessary. Understand the treatment options your doctor may choose during a heart attack.

When to go to the doctor
It is important to seek medical help when chest pain takes more than 20 minutes to relieve, especially when other symptoms such as:
- Dizziness;
- Cold sweats;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Severe headache.
However, in case of cardiovascular disease, such as high blood pressure or heart failure, you should take the medicines prescribed by the cardiologist and only go to the hospital if the pain does not pass after 20 minutes or call the doctor accompanying you.