Pulmonary anthracosis is a type of pneumoconiosis characterized by lung injury caused by the constant inhalation of small particles of charcoal or dust that eventually lodge along the respiratory system, especially in the lungs. Learn what pneumoconiosis is and how to avoid it.
Usually people with pulmonary anthracosis do not show signs or symptoms, going unnoticed most of the time. However, when exposure becomes excessive, there may be pulmonary fibrosis, which can result in respiratory failure. Understand lung fibrosis and how to treat it.

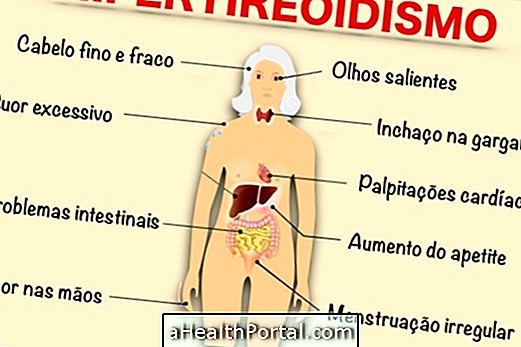
Symptoms of Pulmonary Anthracosis
Although it does not have any characteristic symptoms, anthracosis can be suspected when the person has direct contact with dust, presents dry and persistent cough, in addition to difficulties to breathe. Some habits may also influence the worsening of the person's clinical condition, such as smoking
The people most likely to develop complications of pulmonary anthracosis are the residents of large cities, which usually have heavily polluted air, and coal miners. In the case of miners, to avoid the development of anthracosis, it is recommended to use protective masks, which should be provided by the company, to prevent lung damage, as well as wash hands, arms and face before leaving the work environment.
How is the treatment done?
No specific treatment is required for Pulmonary anthracosis, and it is recommended that only the removal of the person from the activity and sites that have coal dust.
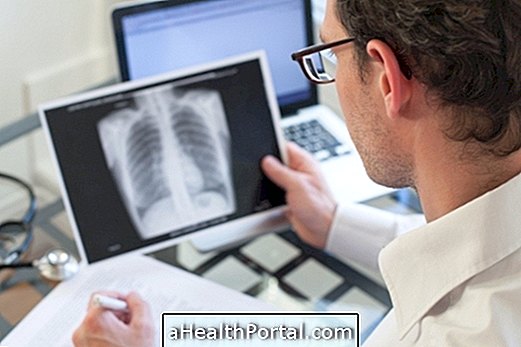
The diagnosis of anthracosis is made through laboratory tests, such as the histopathological examination of the lung, in which a small fragment of the lung tissue is visualized, with the accumulation of charcoal, besides imaging tests such as chest tomography and radiography





-o-que--sintomas-e-tratamento.jpg)