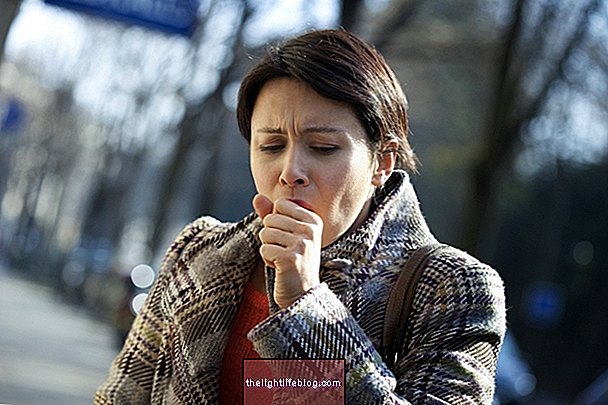
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis corresponds to inflammation of the lungs due to allergic reactions caused by microorganisms, dust or chemical agents, which leads to coughing, difficulty breathing and fever.
Pneumonitis can be classified according to its cause in several types, for example:
- Chemical pneumonitis, the cause of which is the inhalation of dust, toxic or contaminated substances and chemical agents used in the production of synthetic rubber and packaging materials, for example;
- Infectious pneumonitis, which is caused by microorganisms such as fungi due to inhalation of mold, or bacteria and protozoa;
- Lupus pneumonitis, which happens due to autoimmune diseases, being this type more rare;
- Interstitial pneumonitis, which is also called Hamman-Rich Syndrome, is a rare disease of unknown cause that can lead to respiratory failure.
In addition, pneumonitis can be caused by inhaling air contaminated with moldy hay particles, dirty air conditioning, sugar cane residues, moldy cork, moldy barley or malt, cheese mold, infected wheat bran, and contaminated coffee beans, for example.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of inflammation of the lungs are:
- Cough;
- Shortness of breath;
- Fever;
- Loss of weight without apparent cause;
- Respiratory distress;
- Increased respiratory rate, known as tachypnea.
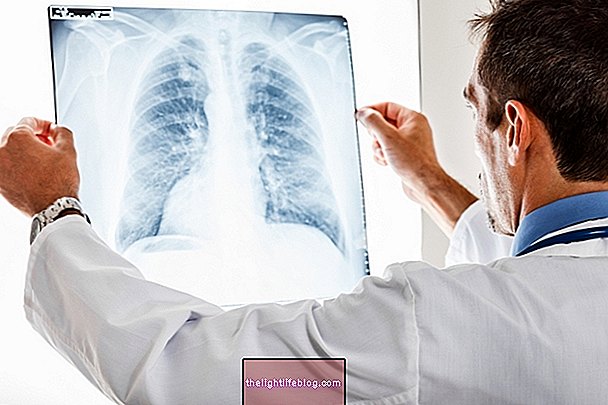
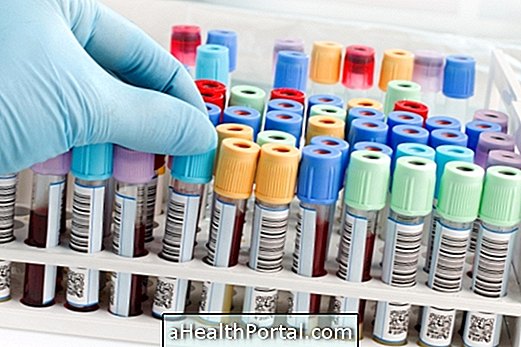
The diagnosis of pneumonitis is made through a clinical evaluation, in addition to the results of some tests, such as lung X-ray, laboratory tests that evaluate lung function and the dosage of some antibodies in the blood. In addition, lung biopsy and bronchoscopy may be requested by the physician for clarification of doubts and conclusion of the diagnosis. Learn what bronchoscopy is and how it is done.
How to treat
The treatment of pneumonitis aims to reduce the person's exposure to the agents that cause the disease, being indicated the withdrawal of work in some cases. In the case of infectious pneumonitis, the use of antibiotics, antifungal or antiparasitic agents may be indicated according to the infectious agent alone.
In some cases the disease undergoes remission within hours, after moving away from the causative agents, although the cure only comes after a few weeks. It is common that, even after the cure of the disease, the patient feels short of breath when exerting physical exertion, due to pulmonary fibrosis that can be installed.
In more severe cases, it may be necessary for the individual to be hospitalized for oxygen and medications to control the allergic reaction.