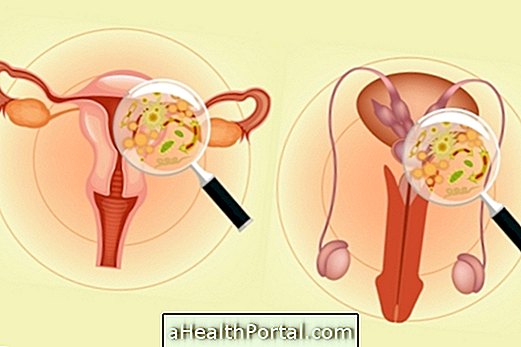
Vaginitis, or vulvovaginitis, is inflammation in the woman's intimate area caused by infections, skin changes in the region, due to menopause or pregnancy, as well as allergies to products or clothing.
Many everyday situations increase the risk of having vaginitis, such as the use of tight pants, frequent use of tampons, and poor hygiene in the area, so avoiding these habits can help ward off this type of inflammation.
The main causes of vulvovaginitis are:
1. Infections
Infections are the main causes of inflammation and vaginal discharge, and are common in women who have several partners, who have used antibiotics, are poor hygienic or have been hospitalized for a long time. The most common are:
Bacterial vaginosis
It is caused by bacteria such as that can multiply inside the vagina, especially after intercourse, menstrual period and causes yellowish discharge and bad odor in the region.
- How to treat : With antibiotics in tablet and vaginal ointments, such as Metronidazole or Clindamycin, prescribed by the gynecologist.
Trichomoniasis
It is an infection caused by the parasite, which is transmitted through unprotected intimate relationships. With this infection, the woman has intense bad smelling, yellowish-green and bullish discharge, besides irritation of the vagina with burning and itching.
- How to treat : With antibiotic tablets, such as Metronidazole or Tinidazole, prescribed by the gynecologist, and the partner should also receive treatment, to avoid new infections;
Candidiasis
It is a yeast infection, usually candida sp ., Which causes a lumpy white discharge in the woman, a lot of itching and redness in the vaginal area, and a frequent urge to urinate. It is most common in women who have low immunity due to stress, use of medications such as corticosteroids or antibiotics, diabetes and HIV infection.
- How to treat : with antifungals in vaginal ointments or tablets, such as Nystatin or Fluconazole, prescribed by the gynecologist.
Cytolytic vaginosis
It is a rarer cause of vaginitis, which causes symptoms very similar to those of candidiasis, and it is important to be screened when the woman has constant itching, burning and white discharge that comes and goes but does not improve with the treatment for candidiasis. It is caused by the proliferation of lactobacillus bacteria, which produces excess acid and causes irritation in the vagina.
- How to treat : Sodium bicarbonate ovules, intravaginal, 3 times a week or baking soda baths are used in the dilution of one tablespoon in 600 ml of water twice a day.
In the presence of these symptoms, one should seek care with a gynecologist to perform the physical examination, for correct diagnosis and indicate the ideal treatment for each case.

2. Allergies
An allergic reaction to any product that is in contact with the intima is also likely to cause inflammation. Some examples are:
- Medicines;
- Intimate cosmetics or perfumed soaps;
- Condom latex;
- Synthetic fabrics of panties;
- Colored or perfumed toilet paper;
- Fabric softeners.
This inflammation causes symptoms such as itching, burning and redness, which can be very uncomfortable and repeated several times until the cause is identified. The treatment is done by avoiding the type of material that causes the allergy, in addition to ointment or tablets based on corticosteroids and antiallergic, prescribed by the gynecologist, to relieve the symptoms.
3. Skin changes
Some conditions can make the skin of the vagina thinner and more sensitive, such as during menopause, the postpartum period, breastfeeding, or when you are being treated with radium or chemotherapy. In these cases, called atrophic vaginitis, the woman may have a yellowish and foul-smelling discharge, in addition to local irritation, dryness, burning and pain during intercourse. The treatment can be done with the use of intimate lubricants, or by the hormonal replacement, that will be indicated by the gynecologist.
In addition, pregnancy also causes changes in the tissue that forms the vagina, due to hormonal oscillations typical of the period, which can cause yellowish discharge and predisposition to infections, especially candidiasis. When the pregnant woman has any of these symptoms, she should report to the obstetrician as soon as possible to see if there is any infection for treatment and follow-up.
How to avoid vaginitis
To avoid this type of inflammation, the woman should take some precautions, such as:
- Avoid wearing tight pants on hot days;
- Sleeping in light clothing or without panties;
- Do not use tampons for many hours at a time;
- Do not douche;
- Avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics;
- Do not have unprotected intimate relationships.
Here are some tips on how to do intimate hygiene and avoid diseases.
Condom use is also important to prevent various types of sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV, hepatitis B and C, gonorrhea, HPV and syphilis, which cause many complications and even death risk. Learn more about these diseases and how to avoid them.