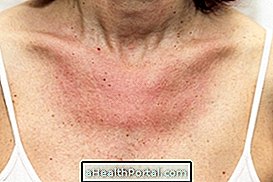
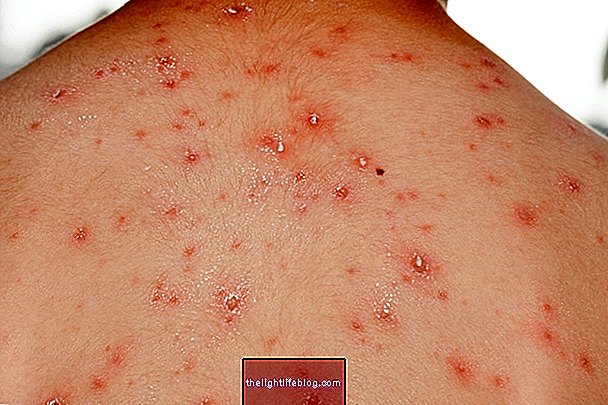
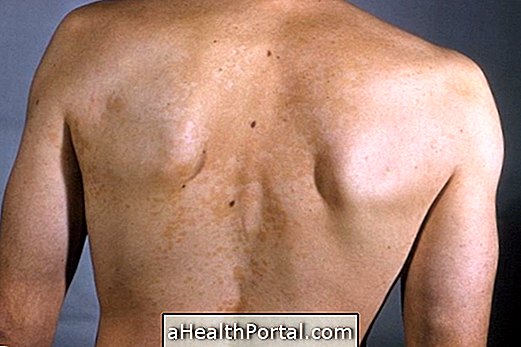
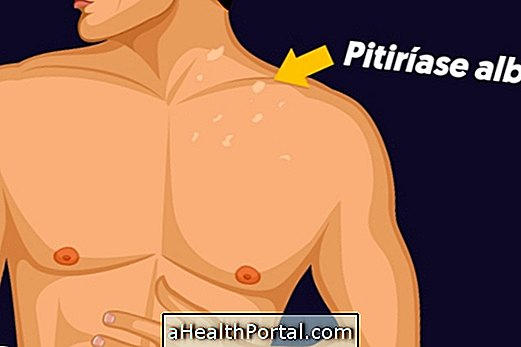
Keratosis pilaris, also known as follicular keratosis or pilaris, is a very common skin disorder that leads to the appearance of slightly hardened red or whitish marbles on the skin, leaving the skin looking like chicken skin.
This change usually does not cause itching or pain and can occur anywhere on the body, although it is more common on the arms, thighs, face and the buttock area.
Follicular keratosis is a mainly genetic condition and therefore has no cure, only treatment, which is usually done through the use of some creams that can help moisturize the skin by disguising the balls.

Creams suitable for treating
The keratosis pilaris usually disapproves over time, however, it is possible to use some creams to disguise this alteration and moisturize the skin. Some of the most recommended dermatologist's creams are:
- Creams with salicylic acid or urea, such as Epydermy or Eucerin, which remove dead skin cells, promoting deeper moisturizing of the skin. The use of these creams may cause slight redness and burning sensation at the application site, but that disappears within minutes;
- Creams with retinoic acid or Vitamin A, such as Nivea or Vitacid, which promote proper hydration of the skin layers, reducing the appearance of balls on the skin.
Usually, pellets of follicular keratosis tend to decrease over time and with the use of these creams. However, it may take several years before they disappear completely, which usually happens after the age of 30.
In addition, it is also important to take other precautions such as avoiding bathing with very hot water, taking no more than 10 minutes, moisturizing the skin after bathing and avoid rubbing clothes and towels on the skin, for example. It is also recommended to avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, to use sunscreen and, in more advanced cases, the dermatologist can indicate the performance of aesthetic procedures, such as chemical peeling and microdermabrasion, for example. Understand what microdermabrasion is and how it is done.
Main causes of follicular keratosis
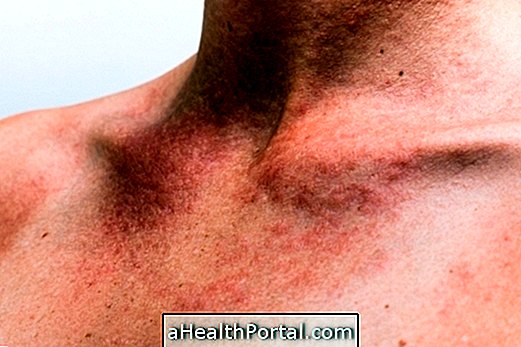
Keratosis pilaris is a mainly genetic condition characterized by excessive production of keratin in the skin and, when left untreated, can progress to spinal-like lesions that can ignite and leave dark patches on the skin.
Although it is a genetic condition, it is benign, leading only to problems related to aesthetics. In addition, some factors may favor the appearance of these polka dots, such as use of tight clothing, dry skin and autoimmune diseases.
People who have allergic diseases, such as asthma or rhinitis, are more likely to develop keratosis pilaris. However, vitamin A deficiency can also lead to its onset, and so it is important to invest in the consumption of vitamin A source foods like cabbage, tomato and carrot, for example. Get to know other foods rich in vitamin A.