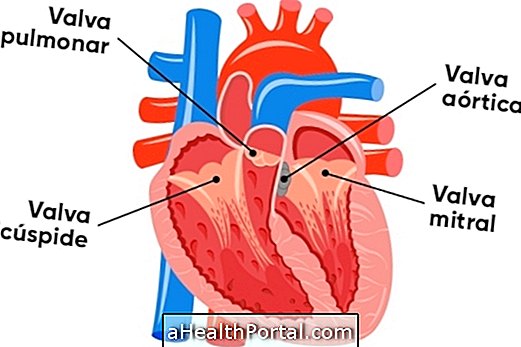
Symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia generally only arise when it is a malignant disease, which causes tiredness and feeling of weakness, dizziness, malaise, fainting, fast or slow heartbeat, a feeling of a lump in the throat, shortness of breath, chest pain, pallor and cold sweat.
These symptoms can affect people with a healthy heart or those with already established heart disease, such as high blood pressure or heart failure, when symptoms may be more pronounced.
Therefore, when you feel these signs or when you have heart problems, it is important to consult with the cardiologist at least once a year to make proper treatment and prevent complications. See 12 signs that can indicate heart problems.

Causes of cardiac arrhythmia
The causes of cardiac arrhythmia are diverse. Among them, we can highlight:
- High pressure;
- Coronary disease;
- Thyroid problems such as hyperthyroidism;
- Chemical imbalances in the blood as altered sodium, potassium or calcium concentration;
- Some medications such as beta-blockers, psychotropic drugs and amphetamines;
- Birth defects of the heart;
- Vigorous physical exercise;
- Complication after cardiac surgery;
- Heart failure or history of heart attack;
- Chagas disease;
- Anemia;
- Aging.
Other factors such as excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol, drugs, cigarettes, anxiety and stress can also precipitate a cardiac arrhythmia.
Treatment for cardiac arrhythmia
Treatment for cardiac arrhythmia will depend on the arrhythmia in question, on the symptoms presented by the patient and on the presence or absence of other heart diseases.
Treatment for benign arrhythmia
In the case of benign cardiac arrhythmia, no treatment is necessary, but the cardiologist may indicate the taking of medications in order to reduce the symptoms of tachycardia and periodic exams.
Treatment for malignant arrhythmia
In case of malignant cardiac arrhythmia the treatment should be based on the type of the arrhythmia being able to be through:
- Medications: propafenone, sotalol, dofetilide, amiodarone and ibutilide;
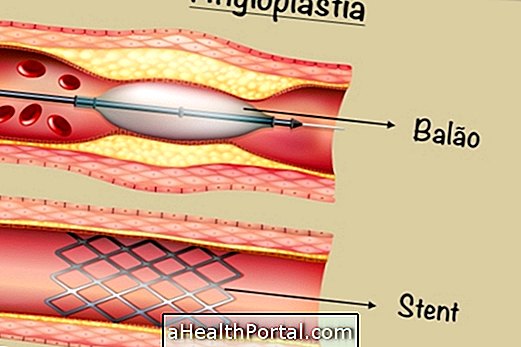
- Pacemaker placement surgery : the device will take control of the heart rate as the doctor prescribes;
- Electric cardioversion : it is used to reorganize the heart rhythm, usually after attempts with injectable drugs;
- Ablation surgery : a type of cauterization, producing an extremely localized and precise burn, which will prevent or hinder new attacks of arrhythmia;
- Change in life habits: stop consuming alcohol, drugs, coffee, coke, some types of tea, cigarettes and drugs.
It is important to note that malignant arrhythmias may worsen with physical exertion, leading to complications such as heart failure and death, so as soon as the symptoms are noticed, a cardiologist should be sought so that the ducts are instituted as soon as possible.
To avoid cardiovascular disease, see 7 tips to decrease the risk of heart attack and stroke.