Knowing what to do in the event of an electric shock is very important as it helps avoiding consequences for the victim, such as severe burns or cardiac arrest, it also helps protect the rescuer from the hazards of electric power.
In these cases, first aid is:
1. Turn off or on the power source, but do not touch the victim;
2. Remove the person from the electrical source that was causing the shock, using nonconductive and dry materials such as wood, plastic, thick cloths or rubber;
3. Call an ambulance by calling 192;
4. Observe whether the person is conscious and breathing;
- If conscious : calm the victim until medical staff arrive;
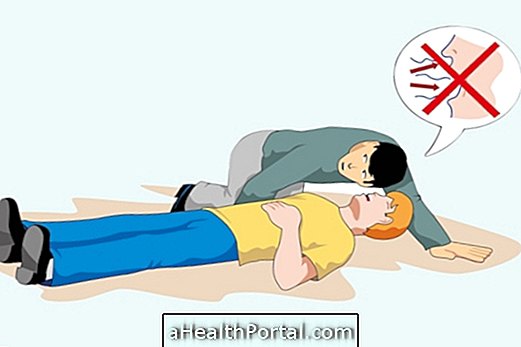
- If you are unconscious, but breathing : put it on its side, placing it in a lateral safety position. Learn how you can do this correctly;
- If you are unconscious and not breathing : start cardiac massage and mouth-to-mouth breathing. See how massage should be done;
5. Continue to the previous step until the arrival of medical help.

The chances of salvage of the electrocuted victim decrease with time and from the 4th minute of receiving the electric shock the chances of survival are less than 50%.
In this way, these first aids should be started as soon as possible, especially the first step, to avoid that the electric current does many damages in the body and results in serious complications.
Main Complications of Electric Shock
In addition to the immediate risk of death, when the current is too high, electric shock can affect the body in other ways, such as:
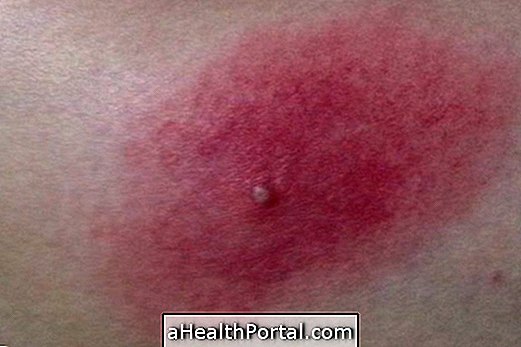
1. Burns
Most accidents with electric shocks only cause minor burns to the skin of the shock site, but when the voltage is too great, too much electricity can affect the internal organs.
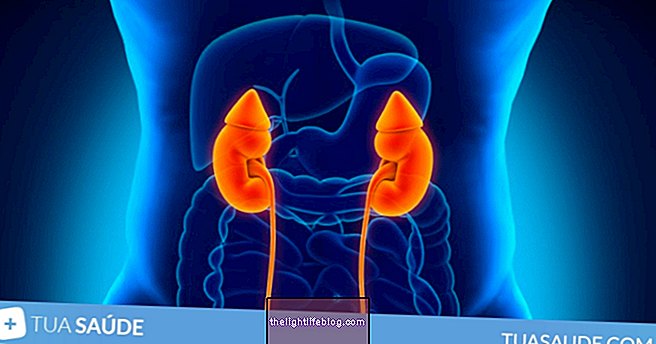
When electricity can reach the internal organs, it can cause serious problems in its functioning and, therefore, the person may need treatment for renal, cardiac or other affected organ failure, for example.
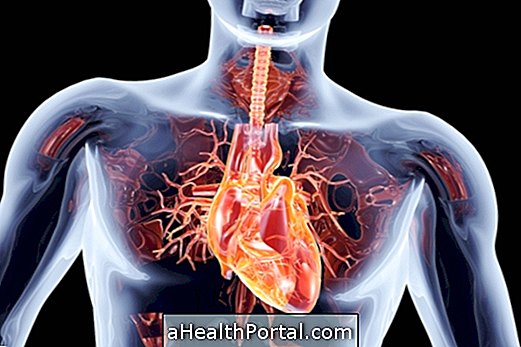
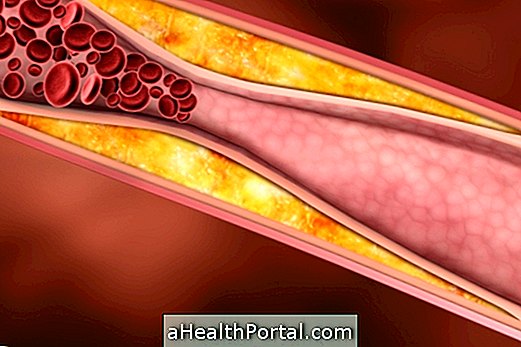
2. Heart problems
When a small electrical current passes through the chest and reaches the heart, it can lead to atrial fibrillation, which is a type of cardiac arrhythmia that must be treated in the hospital to avoid endangering the life of the victim.
Even when the electric current is very high, as in the case of shocks on high voltage posts, the current is so high that it interferes with the electrical activity of the heart and stops the muscle, causing a cardiac arrest that can result in death.
3. Neurological injuries
All electrical currents can affect the nerves in some way, so when there are shocks or very strong shocks, the structure of the nerves can be affected, resulting in neuropathy. Neuropathy can cause symptoms such as pain or numbness in the legs and arms, difficulty in moving muscles or frequent dizziness, for example.







.png)