In case of suspected ovular detachment, where the pregnant woman has persistent colic up to 12 weeks of gestation and excessive bleeding in the first trimester, it is recommended to go immediately to the hospital to have an ultrasound and to evaluate the need to start the treatment, which can be done with rest, water intake, restriction of intimate contact and use of progesterone remedies.
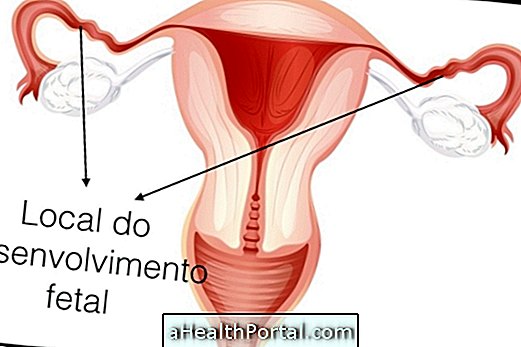
The ovular detachment in pregnancy, scientifically called subcoronic or retrocorionic hematoma, occurs in the first trimester and is characterized by the accumulation of blood between the uterus and the gestational sac.
In mild cases of ovular detachment, the hematoma usually disappears naturally until the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, because it is absorbed by the pregnant organism, but the greater the hematoma, the greater the risk of miscarriage, premature labor and placental detachment .
Treatment for ovular detachment
Treatment for ovular detachment should be started as soon as possible to avoid serious complications such as miscarriage or placental abruption, for example. Generally, ovular detachment decreases and eventually disappears with rest, intake of about 2 liters of water per day, restriction of intimate contact and ingestion of a hormone remedy with progesterone, called Utrogestan.
However, during the treatment the doctor may also advise on other care that the pregnant woman must have for the bruise not to increase and which include:
- Avoid having intimate contact;
- Do not stand too long, preferring to sit or lie down with your legs raised;
- Avoid making efforts, such as cleaning the house and taking care of the children.
In more severe cases, the doctor may still indicate absolute rest, it may be necessary for the pregnant woman to be hospitalized to ensure her health and that of the baby.
Symptoms of ovular detachment
The pregnant woman with ovular detachment does not always present symptoms and, therefore, only the ultrasound examination can identify the hematoma. However, in some cases, the pregnant woman may have symptoms such as vaginal bleeding and colicky-like abdominal pain and therefore, in the presence of these symptoms should go immediately to the hospital.
When to seek medical advice
It is recommended that the pregnant woman call the obstetrician or go to the hospital immediately if she presents the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain;
- Vaginal bleeding;
- Abdominal cramps.
It is not yet known what causes ovular detachment, so it is not possible to prevent its onset. However, taking tests when these symptoms appear helps prevent complications.
See other causes of cramping and bleeding in pregnancy at:
- Colic in pregnancy
- Bleeding in pregnancy








.png)