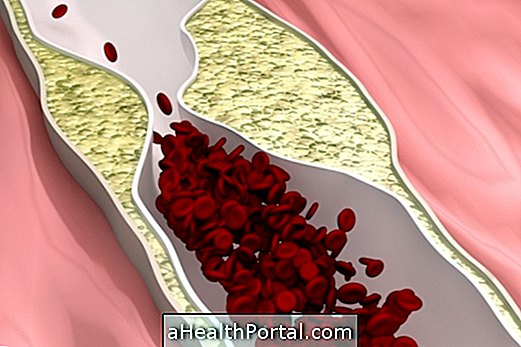
Coronary artery disease is characterized by obstruction of the blood vessels that irrigate the heart, due to the accumulation of fat plaques inside these vessels, which makes it difficult to work the blood to pass to the heart muscle.
In addition, when one of these plaques ruptures, a cascade of inflammatory actions results in an obstruction of the vessel, causing the blood to pass completely through to the heart and causing death of the cardiac tissues with serious complications such as angina pectoris, infarction, arrhythmia, or even sudden death.
Thus, it is important to prevent coronary artery disease from arising or, if it already exists, to make the appropriate treatment so that it does not worsen. For this, it is important to eat a balanced diet and maintain regular practice of exercise. It may still be necessary to use some medications when indicated by the cardiologist.
Main symptoms
Some of the symptoms of coronary heart disease include:
- Constant chest pain;
- Feeling tight in the chest;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Easy tiredness.
Generally, these signs are difficult to identify and thus it is very common that the disease is only identified when it is in a very developed degree or when it causes some serious complication, such as infarction.
In addition, people with risk factors such as high cholesterol, diabetes or a sedentary lifestyle are at increased risk of having the disease, so they should have frequent checkups with the cardiologist to identify if they are at risk for a serious complication, starting with treatment as needed.
What tests to diagnose
The diagnosis of coronary disease can be made by the cardiologist through examinations such as coronary angiography, electrocardiogram, computed tomography of the heart or physical exercise test.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for coronary heart disease includes regularly exercising, releasing stress and eating well, avoiding too much fatty or sugary foods, and avoiding other risk factors for the disease, such as smoking or drinking alcohol, for example.
For this, usually the treatment is guided by a cardiologist, who also assesses the need to start using medication to control cholesterol, hypertension or diabetes. These medicines should be used as directed and for life.
In the more severe cases, cardiac catheterization and, if necessary, angioplasty may be necessary for the placement of a network within the vessel or even a revascularization surgery with placement of the breast and saphenous bridges.
Prevention of coronary heart disease
Prevention of coronary heart disease can be done through good living habits such as quitting smoking, eating properly, doing physical activity, and lowering cholesterol levels. The proper levels of cholesterol are:
- HDL : above 60 mg / dl;
- LDL : below 130 mg / dl; being below 70 for patients who have already infarcted or who have diabetes, high blood pressure or smoke, for example.
Those at high risk of developing coronary heart disease, in addition to adopting a healthy lifestyle, should also follow up with a cardiologist at least once or twice a year.