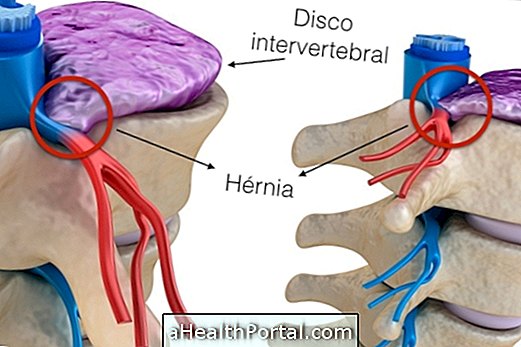
The main symptom of a herniated disk is pain in the spine that usually appears in the region where the hernia is located, and may be in the cervical, lumbar or thoracic spine, for example. In addition, the pain can follow the path of the nerves of the region, so it can even radiate to more distant places, reaching legs or arms.
Other symptoms that may occur in the herniated disc are tingling, numbness, pinching or, in more severe cases, to decreased force or urinary incontinence. However, it should be remembered that herniated discs do not always cause symptoms or may only cause mild discomfort.
The disc herniation arises when the intervertebral disc and its gelatinous center, which function as a kind of shock absorber of the spine, leave the correct place, causing the compression of nerves of the region. The treatment is done with medicines to relieve the pain, physiotherapy or, in some cases, surgery. If you want to understand how a herniated disc is formed and how to treat it, check out All about Herniated Disc.
Main symptoms
The symptoms of herniated disc vary according to its location, and the most common are:
1. Symptoms of cervical disc herniation
In this type, the pain is located in the upper part of the spine, more specifically in the neck. Nerve compression can cause pain to radiate to the shoulder or arm. Other symptoms include:
- Difficulty in making movements with the neck;
- Sensation of numbness or tingling in the shoulder, arm, elbow, hand or fingers;
- Decrease in strength in one arm.
Symptoms of herniated disc may be different from one individual to another as it depends on its location and intensity of compression. These symptoms may suddenly appear, disappear spontaneously, and return at unpredictable intervals. But they can also be constant and long lasting.
2. Symptoms of lumbar disc herniation
When this type of hernia happens it is common to have an intense back pain. But other symptoms are:
- Pain along the path of the sciatic nerve that runs from the spine to the buttock, thigh, leg and heel;
- There may be weakness in the legs;
- Difficulty in raising the foot by leaving the heel on the floor;
- Change in functioning of the bowel or bladder by nerve compression.
The amount and intensity of symptoms depends on the location and intensity of nerve involvement. Generally, loss of strength indicates severe alteration and should be quickly evaluated by the orthopedist or neurosurgeon.
3. Symptoms of herniated disc thoracic
The thoracic disc herniation is less common, occurring in only 5% of the cases, but when it arises it can cause:
- Pain in the central region of the spine radiating to the ribs;
- Pain to breathe or move with the chest;
- Pain or change in sensation in the belly, back or legs;
- Urinary incontinence.
When these symptoms that indicate herniated disc appear, it is recommended to seek an orthopedist or neurosurgeon to make an evaluation and ask for an x-ray, MRI, or spinal CT scan.
Depending on the outcome of the tests, the treatment can be done with physiotherapy or surgery, according to the needs of each person and the severity of the problem. Learn more about how this type of problem is treated.

Who has a higher risk of a herniated disc
The main cause for the development of a herniated disc is progressive wear of the intervertebral discs that lie between each two vertebrae of the spine. Thus, this problem is more common in people over 45 due to the natural aging process.
In addition, disc hernias are also more frequent in workers who need to lift heavy objects often, such as construction workers. People who suffer from spinal injuries, who make repetitive efforts without guidance or who suffer some inflammation or infection in the spine are also more likely to develop this alteration.
How to Prevent Herniated Disc
Most cases of herniated disc are caused by a person's genetic predisposition, but their formation is also influenced by a number of factors, such as sedentary lifestyle and inadequate physical exertion, such as making jerky movements, incorrectly or lifting a lot of weight. Thus, to prevent the formation of a herniated disc, it is important to:
- Practice regular physical activities;
- Do stretching and strengthening exercises of the abdomen muscles;
- Maintain correct posture, especially when lifting heavy objects. It is advised to take heavy objects by folding the legs, to distribute the weight, preventing it being applied mainly in the vertebral column;
- Be aware of proper posture while sleeping, sitting or standing for a long time. See tips on how to choose the best mattress and pillow to maintain good posture at night.
See, in the video below, these and other tips, guided by the physiotherapist: