Changes in thyroid can cause several symptoms, which if not well interpreted may go unnoticed and the problem may continue to worsen. When thyroid function is altered, this gland may be overworked, also known as hyperthyroidism, or may be working poorly, which is also known as hypothyroidism.
While hyperthyroidism can cause symptoms such as agitation, nervousness, difficulty concentrating, and weight loss, hypothyroidism causes symptoms such as tiredness, memory loss, ease of getting fat, dry and cold skin, irregular menstrual cycle and hair loss. However, there are some general symptoms that you may be aware of as they may indicate problems or changes in the functioning of your thyroid gland such as:
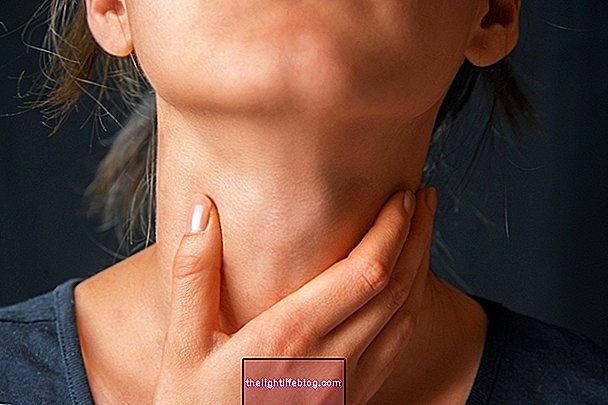
1. Neck and neck discomfort
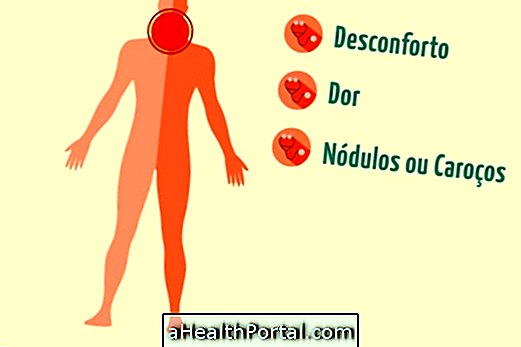
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, so if you experience pain, discomfort or the presence of a lump or lump in your neck, it may be indicative that the gland is altered, which may interfere with its good operation.
As soon as you notice any thyroid-related changes, it is important to go to the general practitioner or endocrinologist for diagnostic tests. Learn how to do thyroid self-examination to identify any type of change.
2. Difficulties of concentration and forgetfulness

Feeling that you are constantly with your head out of place, often having concentration difficulties or constant forgetfulness, may be a symptom of abnormalities in thyroid function, lack of concentration may be a sign of hyperthyroidism and forgetfulness a sign of hypothyroidism. Look at the symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
3. Hair loss and dry skin

Hair loss is normal especially in the fall and spring, but if this hair loss becomes too pronounced or prolongs beyond these times, this may indicate that there is some change in the functioning of the thyroid. In addition, dry and itchy skin may be indicative of thyroid problems, especially if these symptoms are not related to cold and dry weather.
4. Weight gain or loss

Weight gain for no apparent reason, especially if there were no changes in diet or day-to-day activities, is always worrying and can be caused by hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland is working poorly and slows down the entire body. However, weight loss may also occur for no apparent reason, which may be related to hyperthyroidism and the presence of Graves' Disease, for example. See all the symptoms here.
5. Drowsiness, Tiredness and Muscle Aches

Drowsiness, constant tiredness and an increase in the number of hours you sleep per night can be a sign of hypothyroidism, which slows down the body's functions and causes a constant feeling of fatigue. In addition, unexplained muscle aches or tingling can also be another sign, as a lack of thyroid hormone can damage the nerves that send signals from the brain to the rest of your body, triggering tingling and twinging in the body.
6. Mood Changes and Belly Pruning

Deficiency or excess of thyroid hormones in the body can cause mood changes, and hyperthyroidism can lead to irritability, anxiety and restlessness, whereas hypothyroidism can cause constant sadness or depression due to altered levels of serotonin in the brain.
In addition, changes in the functioning of the thyroid can also cause difficulties in digestion and constipation, which can not be resolved with diet and exercise.
7. Palpitations and High Pressure

The palpitations that sometimes make the pulse in the neck and pulse feel like a symptom that the thyroid is not working as it should. In addition, high blood pressure may be another symptom, especially if it does not improve with exercise and diet, hypothyroidism can also cause an increase in bad cholesterol levels in the body.
In addition to these symptoms, loss of sexual desire and lack of libido can also be an indication that your thyroid is working poorly, as well as weight gain, hair loss and muscle aches.
If any of these symptoms are noticed, it is important that you see an endocrinologist as soon as possible so that he can order blood tests that measure thyroid hormone levels in the body or a thyroid ultrasound to check for the existence and size of possible nodules.
How to treat thyroid changes
Treatment for thyroid problems, such as inflamed or altered thyroid, includes the use of medications that regulate thyroid function or surgery to remove the gland, and it is necessary to have hormone replacement therapy for a lifetime. See which remedies are used to treat thyroid problems.
Watch the following video on how eating can help:

Thyroid changes during pregnancy
Those who have hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism may find it more difficult to get pregnant and have a higher risk of spontaneous abortion and low IQ in the baby; in women there is a higher risk of eclampsia, preterm birth and placenta previa.
Normally those who are trying to get pregnant should be able to normalize thyroid values with the use of endocrinologist-prescribed medications and maintain proper control during pregnancy to decrease the chances of complications.
Adequate food and resort to the use of herbal teas can also help control the functioning of this gland. Here's what to eat to regulate the thyroid.