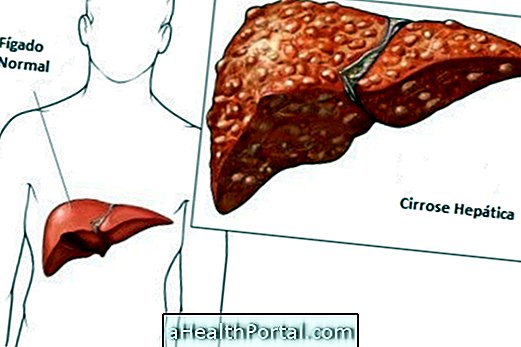
Liver cirrhosis is a disease in which there is chronic and progressive inflammation of the liver which is characterized by weakness, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin and eyes, appearance of vascular spiders and swollen abdomen.
It is important that this disease is diagnosed as soon as the symptoms appear, so that there are no complications. The diagnosis is made through laboratory tests that mainly evaluate liver function and imaging for the organ to be observed. Learn more about cirrhosis.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
People who are in the early stages of cirrhosis usually do not have symptoms, but in slightly more advanced cases there may be several symptoms, such as:
- Weakness;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Lack of appetite;
- Nausea;
- Loss of weight without apparent cause;
- Skin and yellow eyes;
- Itching all over the body;
- Swollen abdomen;
- Vomiting with blood due to bleeding from esophageal varices;
- Swelling of the legs;
- Renal insufficiency;
- Malnutrition in advanced cases;
- Muscle atrophy;
- Flushing of the palms;
- Flexion of the fingers;
- Vascular spiders, which are spider veins under the skin;
- Increased breasts in men;
- Increase of the salivary glands located at the level of the cheeks;
- Testicular atrophy;
- Peripheral neuropathy, which is the disturbance of the joints of the nervous system.
When any of these symptoms are noted, it is important to consult the hepatologist or a general practitioner because it may be cirrhosis and treatment should be started quickly.
Cirrhosis is characterized by progressive inflammation of the liver and may be caused by overuse of alcohol or drugs, viral infections, and genetic diseases such as hemochromatosis and Budd-Chiari syndrome. See which are the 9 leading causes of cirrhosis.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of liver cirrhosis is made by the general practitioner or hepatologist by assessing symptoms, habits of the person and laboratory tests that assess liver function, kidneys and coagulation capacity, as well as serological tests to identify viral infections. See which exams evaluate the liver.
In addition, to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may order imaging tests such as CT or MRI to evaluate the liver and abdominal region. Liver biopsy is not done for the purpose of diagnosis, but rather to determine the severity, extent, and cause of cirrhosis. Know when it is indicated and how the liver biopsy is done.
Treatment for cirrhosis
The treatment for cirrhosis varies according to the cause, and can be done with the suspension of the drug or alcohol, for example. In addition, it is important to maintain a proper diet and that includes vitamin supplementation. Learn how the cirrhosis diet is made.
It is also important to treat complications as they arise. One treatment option is liver transplantation, which is usually done in more severe cases. Understand how the treatment is done for cirrhosis.