Respiratory tract infection is an infection that occurs in any region of the respiratory tract, reaching from the upper or upper airways, such as the nostrils, throat or bones of the face, to the lower or lower airways, such as bronchi and lungs.
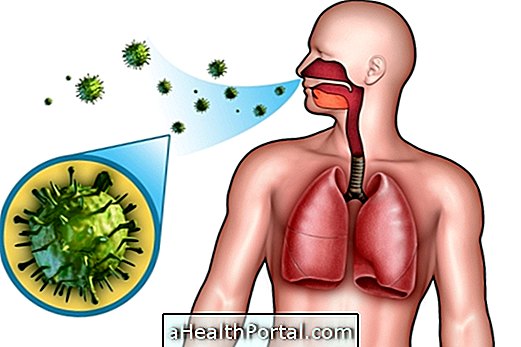
Generally, this type of infection is caused by microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria or fungi of various types, causing symptoms such as coryza, sneezing, coughing, fever or sore throat, for example. These infections are more common in winter because it is the period when there is more circulation of microorganisms, since the temperature is lower and there is a greater tendency to stay indoors. Find out what are the most common winter diseases and how to avoid them.
High respiratory infections are the most common and are usually contagious, especially those caused by viruses, which are easily spread in crowded places such as schools, day care centers or on the bus, for example. Low infections, which reach the bronchi and lungs, are often more severe and reach people at greater risk, such as infants, children, the elderly, and people with compromised immunity.

What can cause
There is not only one type of respiratory infection, but several infections that can reach the respiratory tract, some lighter and others more serious. Some of the most common causes of respiratory infections include:
- Common cold or flu : it is an infection caused by viruses, causing cough, runny nose, sneezing and nasal obstruction. In influenza, there is infection by influenza-like viruses, which cause more intense symptoms, such as body pain and fever. Understand the differences between flu and cold, and what to do to relieve it;
- Sinusitis : is the infection caused in the bones of the face, which can cause headache, facial pain, nasal discharge, cough and fever caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi;
- Pharyngitis : There is infection of the throat region, causing local inflammation, in addition to coryza and cough, most often caused by viruses;
- Tonsillitis : Pharyngitis can be accompanied by infections of the tonsils, causing intense inflammation, being more intense when there is infection by bacteria, that can produce pus in the region;
- Bronchitis : is inflammation of the bronchi, already considered a low respiratory infection, since it already reaches the lungs. It causes coughing and shortness of breath, and can have both allergic and infectious causes of viruses or bacteria. Understand better what is bronchitis and the major types;
- Pneumonia : is the infection of the lungs and lung alveoli, which can cause intense secretion, coughing, shortness of breath and fever. It is usually caused by bacteria, also can be caused by viruses or fungi;
- Tuberculosis : A type of lung infection caused by Koch's bacillus bacteria, which causes chronic, gradual inflammation with cough, fever, weight loss and weakness, which can become serious if treatment is not done soon. Learn to identify the symptoms of tuberculosis and how to treat it.
These infections can be classified as acute, when they appear suddenly and have a rapid worsening, or as chronic, when it has a long duration, of dragged evolution and difficult treatment, which usually happens in certain cases of sinusitis, bronchitis or tuberculosis, for example.
How to confirm
To diagnose the respiratory infection, usually, only the doctor's evaluation is necessary, that will identify the symptoms and make the physical evaluation, like auscultation of the lungs and observation of the pharynx, for example.
In cases of suspected more serious infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, or when there are doubts about the cause, it may be necessary to perform tests, such as chest X-rays, blood tests or sputum tests, to identify the microorganism that caused the infection and so decide for the most appropriate treatment.

Main symptoms
The most common symptoms of respiratory infection are:
- Coriza;
- Cough, which may contain secretion or not;
- Obstruction of the nostrils by secretion;
- Malaise;
- Fever;
- Chest pain;
- Headache;
- There may be ear pain;
- There may be conjunctivitis.
Shortness of breath may occur in some cases. However, this is a sign that the condition can be serious. An evaluation should be made when the doctor first identifies the causes and indicates the best form of treatment.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of respiratory infection depends on its cause and the severity of the infection. Thus, it is usually indicated rest, use of analgesics and antipyretics, such as Dipirone or Paracetamol, and plenty of hydration throughout the day.
For example, antibiotics such as Amoxicillin or Azithromycin are only indicated in cases of suspected bacterial infection, which is most common in high fever situations, when the infection persists for more than 7-10 days or when there is pneumonia.
Antifungal agents may also be used, also only when it is suspected that the cause of infection is due to fungi.
In addition, people hospitalized may need respiratory physiotherapy to remove lung secretions and so relieve the discomfort that the disease causes.
How to avoid
To avoid respiratory infections, it is recommended to avoid crowded places, contact with infected people and always wash hands and avoid putting objects in the nose or mouth as they are the main forms of contagion.
It is also recommended to keep the immune system balanced, which is facilitated with a balanced diet, rich in vegetables, grains and antioxidants, such as vitamin C, present in fruits. Also, avoid very humid environments with excess dust, molds and mites is recommended to avoid allergies, which can be accompanied by an infection.
Check out some attitudes that help prevent respiratory diseases.







-o-que--sintomas-e-tratamento.jpg)