Testosterone is the main male hormone, responsible for features such as beard growth, thickening of the voice and increased muscle mass, as well as stimulate the production of spermatozoa, being directly related to male fertility. In addition, testosterone is also present in women, but in lesser amounts.
After the age of 50, a decrease in testosterone production is common, and andropause, which is similar to the menopause of women, is characterized. However, the decrease in the production of testosterone in man does not mean that it becomes infertile, but rather that its reproductive capacity may be diminished, since the production of spermatozoa is compromised. Learn more about andropause.
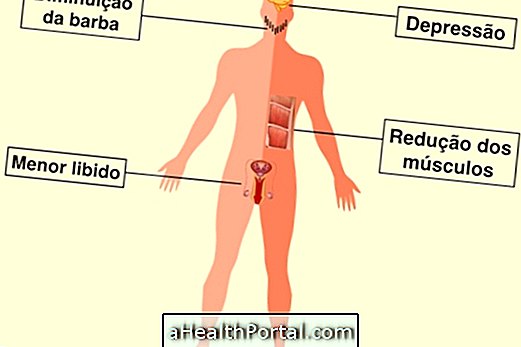
Signs of Low Testosterone
In men, decreased testosterone production can lead to the following symptoms:
- Decreased libido;
- Lower sexual performance;
- Depression;
- Decreased muscle mass;
- Increased body fat;
- Decreased beard and loss of hair in general.
In addition to sexual dysfunction, low testosterone in men can also cause problems such as osteopenia, osteoporosis and altered male fertility. Decreased hormone production is common and occurs especially with excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, when a man smokes, is overweight or has diabetes.
Testosterone is also present in women, but in lower concentrations. However, when testosterone levels decline in women there may also be the onset of some symptoms, such as:
- Loss of muscle mass;
- Accumulation of visceral fat;
- Decreased sexual desire;
- Generalized disinterest, which can be mistaken for depression in some cases.
On the other hand, when testosterone levels are elevated in women, there may be the development of typically male characteristics, such as hair growth on the chest, face and inner thighs, near the groin.
When symptoms appear that may be related to altered testosterone levels, it is important to consult an endocrinologist, urologist, for men, or gynecologist for women. Thus, one can verify the production of this hormone and, if necessary, initiate the treatment. Learn what to do to increase testosterone production.

Testosterone Testing
Tests that indicate the amount of testosterone in the body are not specific and are not always reliable because their values change constantly according to ethnicity, age and lifestyle, such as healthy eating and physical activity or physical inactivity. Therefore, the doctor does not always ask for the test to evaluate your bloodstream concentration based solely on the symptoms that the person presents.
Usually the dosage of free testosterone and total testosterone is required. Free testosterone represents the concentration of testosterone that is available in the body and can be absorbed and thus fulfills its function in the body and corresponds to 2 to 3% of total testosterone, which corresponds to the total amount of testosterone produced by the body, or free testosterone and testosterone that is bound to proteins.
The normal values of total testosterone in the blood are:
- Men: 241 - 827 ng / dL
- Women: 14-76 ng / dL
Regarding the reference values of free testosterone in the blood, in addition to varying according to the laboratory, they vary according to the age and phase of the menstrual cycle, in the case in the women:
- Men's
| Age | Reference values |
| Up to 17 years | Not established |
| Between 17 and 40 years | 3 - 25 ng / dL |
| Between 41 and 60 years | 2.7 - 18 ng / dL |
| Over 60 years | 1.9 - 19 ng / dL |
- Women
| Stage of the menstrual cycle | Reference values |
| Follicular phase | 0.2 - 1.7 ng / dL |
| Middle of the cycle | 0.3 - 2.3 ng / dL |
| Luteal phase | 0.17 - 1.9 ng / dL |
| Post menopause | 0.2 - 2.06 ng / dL |
Testosterone may be increased in the case of precocious puberty, adrenal hyperplasia, trophoblastic disease during pregnancy, ovarian cancer, cirrhosis, hyperthyroidism, use of seizure medications, barbiturates, estrogens or use of the contraceptive pill.
However, testosterone may be decreased in cases of hypogonadism, testicular withdrawal, Klinefelter's syndrome, uremia, hemodialysis, hepatic insufficiency, excessive consumption of alcohol by men and use of drugs such as digoxin, spironolactone and acarbose.

How to Increase Testosterone
Testosterone supplements should be used under medical indication and can be found in the form of tablets, gel, cream or transdermal patch. Some trade names are durateston, somatrodol, provacyl and androgel.
In man
When testosterone is below recommended levels and man has signs and symptoms of decreased testosterone production, the urologist may prescribe the use of testosterone in the form of tablets, an injection, or a gel to be used as prescribed.
The effects of testosterone on men can be observed in 1 month of treatment and with this he must present himself more confident, with greater sexual desire, greater muscular rigidity and feeling stronger. Thus, testosterone supplementation may be indicated during andropause to decrease its effects, improving the quality of life of the man.
The use of testosterone should be recommended by the doctor as it can lead to health problems such as liver fat, high cholesterol, high blood pressure and atherosclerosis. See how male hormone replacement is done and possible side effects.
In woman
When the amount of testosterone the woman has is very low, the gynecologist can observe these symptoms and request the test to evaluate their concentration in the blood.
Testosterone supplementation is indicated only in cases of androgen deficiency syndrome or when the ovaries stop working due to ovarian cancer, for example. When the decrease in testosterone in women is caused by another reason it is more appropriate to try to balance the hormone levels by increasing the estrogen.