Curettage is a procedure performed by the gynecologist that serves as a treatment to cleanse the uterus from the remains of an incomplete abortion, from the placenta after normal delivery or as a means of diagnosis, in which case it is called a semiotic curettage.
Curettage is very painful procedure but throughout the procedure the woman should be sedated or anesthetized and therefore feel no pain. However, abdominal pain or discomfort can remain for about 10 days but analgesics such as Dipirone or Ibuprofen can be taken to decrease pain and discomfort.
How curettage is done
Uterine curettage can be done in a clinic or hospital by introducing a curette, a surgical instrument, into the vagina and scraping the walls of the uterus. Another form of curettage is the introduction of an aspiration cannula which is a vacuum mechanism, which sucks up any uterine contents.
Usually the doctor chooses to use the two techniques in the same procedure, starting with the vacuum initially and then scraping the walls of the uterus to remove the contents faster and safer. This procedure can be done under local anesthesia, when it is used as a diagnostic test, or general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia, when it is used to clean up remnants of an abortion, for example.
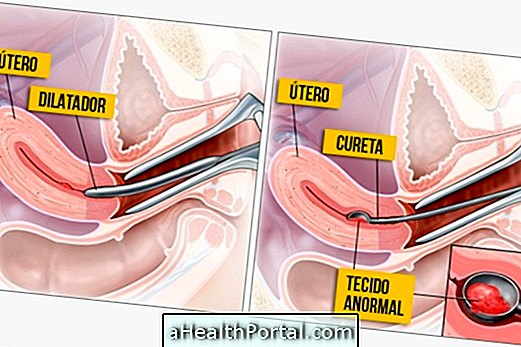
This scraping of the walls of the uterus can be done with or without previous dilatation of the cervical canal depending on the size of the contents that will be removed and during any procedure the doctor should observe the inside of the uterus on a screen. Generally, rods of increasing thickness are used until the curette is allowed to enter and exit without injuring the uterine cervix and walls of the uterus.
The woman should be observed for a few hours, but there is no need for hospital admission, unless there is some complication. After the procedure the woman can go home, but she should not drive because she must be sleepy or have a headache due to sedation.
When it is indicated
Uterine curettage may be indicated for the following conditions:
- Removal of ovary remains in case of abortion;
- Removal of placental remains after normal delivery;
- To remove the egg without embryo;
- To remove uterine polyps;
- Retention or infected abortion, when the remains are there for more than 8 weeks;
- When the embryo does not develop properly, as in the hydatidiform mole.
Before starting curettage the doctor may indicate the use of a medicine called Misoprostol that induces uterine contraction, facilitating the withdrawal of its contents. This care is especially useful when you need to remove the remains of a fetus longer than 12 weeks or longer than 16 cm.
The use of this medicine should only be done within the clinic or hospital, hours before starting curettage.
Find out about curettage recovery and the necessary care to follow.