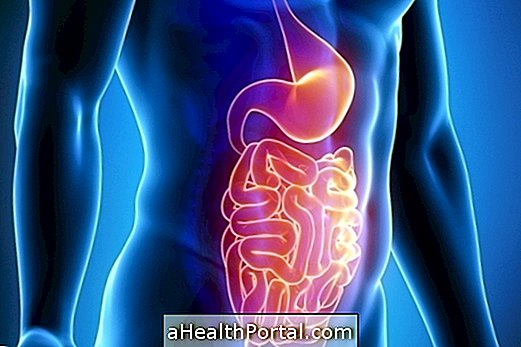
The stone in the gallbladder, scientifically called a gallstone or cholelithiasis, is the accumulation of calcium and cholesterol inside the gallbladder caused by high blood cholesterol levels, poor diet, obesity or diabetes, for example.
The stones can arise in three situations involving bile, which is a liquid produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder that is responsible for assisting in the digestion process of fat:
- Bile with too much cholesterol: excess cholesterol in bile can not be eliminated, leading to the formation of stones;
- Bile with a lot of bilirubin: it happens when there are problems in the liver or in the blood, leading to the high production of bilirubin;
- Concentrated bile: it happens when the gallbladder can not eliminate its content, which makes the bile very concentrated and favors the formation of stones in the gallbladder.
Generally, the stones in the gallbladder do not cause symptoms and, therefore, do not require treatment, being eliminated by the feces. However, when they are very large, they can become trapped in the bile ducts and cause inflammation in the gallbladder, characterized by severe abdominal pain that can last up to 5 hours. Here are the 6 stone symptoms in the gallbladder.
Cholelithiasis is not serious and can usually be treated with the use of medicines and a diet low in fat, and surgery for gallstone is only used in the most severe cases.
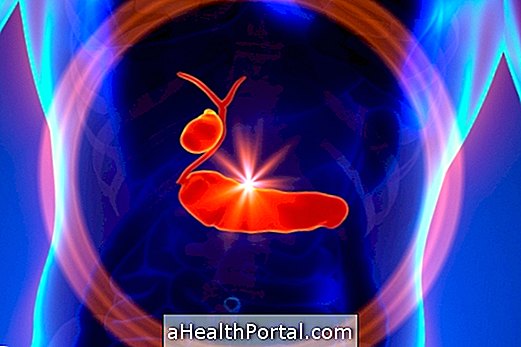
7 leading causes of gallstone
-
High fat diet: Bile is responsible for assisting in the process of fat digestion, however, in a diet rich in fat and low in fiber, the digestion of fat ends up not being complete because there is an excess. Thus, the formation of cholesterol stones in the gallbladder occurs more easily, which are the most common types of stone to appear. See what LDL cholesterol is and how to lower it.
Overweight or obese: Obese or overweight people usually have high rates of LDL, also called bad cholesterol, and bile is unable to dissolve all cholesterol, which favors the formation of gallstones.
Cirrhosis: In cirrhosis, the production of bile by the liver is impaired, bile being unable to perform its role in the body and favoring the formation of gallstones. Cirrhosis can be caused both by excessive alcohol consumption and prolonged use of medications, such as ceftriaxone, which is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections and should be given with care to people who have liver problems because of their toxicity . Understand a little more about cirrhosis.
Sedentary: The sedentary person is one who does no physical activity, which favors the accumulation of abdominal fat and increase of cholesterol, leading to the formation of stones. Check out 5 tips to get out of sedentary lifestyle.
Diabetes mellitus: In diabetes there is a high concentration of triglycerides, which increases the chances of stones appearing. Understand what diabetes mellitus treatment is and how it is done.
Pregnancy: The presence of stone in the gallbladder are more frequent during pregnancy, because the hormonal changes reduce the speed of emptying of the gallbladder, facilitating the accumulation of cholesterol in its interior. Learn more about the gallstone in pregnancy.
Prolonged Use of Contraceptives: The use of contraceptives can increase the amount of estrogen, which stimulates cholesterol precipitation and relaxation of the gallbladder, promoting the sedimentation of cholesterol and salts. Thus, women are more likely to have gallstones.
When to go to the doctor
It is recommended to go to the doctor when symptoms appear that can last more than 1 hour, such as:
- Abdominal pain on the right side after a meal;
- Fever above 38º C and headache;
- Back pain;
- Nauseation and vomiting;
- Skin and yellow eyes;
- Diarrhea and gas;
- Loss of appetite.
Treatment for stone in the gallbladder should be done by a gastroenterologist when the patient has symptoms and usually includes the use of shock waves or gallstone remedies, such as Ursodiol, that help to destroy and dissolve the stone, through the stool. Learn more about treatment for gallstone.
In more severe cases, where the patient has frequent biliary crises or intense symptoms, surgery may be necessary to remove the gallbladder and reduce the chances of forming new stones.
In addition, it is also recommended that patients with cholelithiasis eat a low-fat diet by avoiding fried foods, sausages or salty snacks, which can lead to increased stones and discomfort. Here are some tips on what you can and should not eat during the gallbladder stone treatment: