Down syndrome, or trisomy 21, is a genetic disease caused by a mutation in chromosome 21 that causes the carrier not to have a pair, but a trio of chromosomes, and therefore in total it does not have 46 chromosomes, but 47.
This change in chromosome 21 causes the child to be born with specific characteristics, such as lower implantation of the ears, eyes pulled up and a large tongue, for example. Learn about other features of this syndrome.
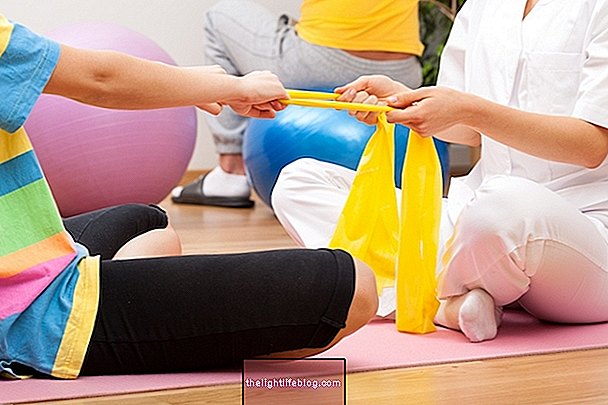
As Down syndrome is the result of a genetic mutation, it has no cure, and there is no specific treatment for it. However, some treatments such as physiotherapy, psychomotor stimulation and speech therapy are important to stimulate and assist in the development of the child with trisomy 21.

Main features
Some of the characteristics of Down syndrome patients include:
- Implantation of the ears lower than normal;
- Large and heavy tongue;
- Eyes pulled up;
- Delay in motor development;
- Muscle weakness;
- Presence of only 1 line in the palm of the hand;
- Mild or moderate mental retardation;
- Short stature;
- Overweight;
- Delay in language development.
The child with Down syndrome does not always have all these characteristics, and it may happen that some children have only one of these characteristics, not considering in these cases, who have the disease. Understand how the diagnosis of Down syndrome is made.
Causes of Down syndrome
Down syndrome occurs due to a genetic mutation that causes an extra copy of part of chromosome 21 to happen, resulting in changes in development.
This mutation is not hereditary, that is, it does not pass from father to son and its appearance may be associated with the age of the parents, but mainly of the mother, with a greater risk in women who became pregnant with more than 35 years of age, since the likelihood of genetic changes increases from that age.

How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of this syndrome is usually made during pregnancy, through the performance of some tests such as ultrasound, nuchal translucency, cordocentesis and amniocentesis, for example. Learn more about the diagnosis of Down syndrome in pregnancy.
After birth, the diagnosis of the syndrome can be confirmed by observing the characteristics presented by the baby and carrying out a blood test, in which an evaluation of the chromosomes is made to observe the presence of mutations and the presence of extra chromosomes.
Treatment for Down syndrome
The treatment for Down syndrome aims to promote the child's development, promoting their quality of life. Thus, it is recommended that physiotherapy sessions, psychomotor stimulation and speech therapy are carried out to facilitate speech and eating.
Babies with this syndrome should be monitored from birth and throughout life, so that their health status can be regularly assessed, because this chromosomal change increases the risk of developing heart and respiratory diseases, sleep apnea and thyroid changes.
In addition, the child may have some type of learning difficulty, but does not always have significant mental retardation. Then you can develop, study and even work. Life expectancy today is more than 40 years and during those years, people with Down syndrome may need specialized health care, which must be individualized, and may also be accompanied by other specialties, such as cardiology or endocrinology, for example.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther