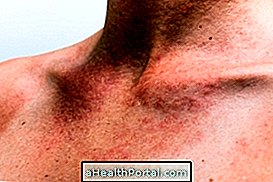
The cyst in the head is usually a benign tumor that can be filled by fluid, tissue, blood or air and usually appears during pregnancy, shortly after birth or throughout life and can occur in both the skin and the brain. The cyst in the head may disappear, increase in size or generate symptoms when it is located in the brain, such as headache, nausea, dizziness and balance problems.
Diagnosis of the cyst in the head is made by a neurologist in the case of a cyst in the brain and can be performed during pregnancy by ultrasonography or after the appearance of the first symptoms through computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. The skin cyst is diagnosed by a dermatologist by means of assessing the characteristics of the cyst. After the diagnosis, there should be medical follow-up, because depending on the size and symptoms caused by the cyst, removal may be indicated by surgery.
Main types of cyst in the head
Cysts in the head are usually formed during gestation but may also appear due to a blow to the head or infections in the brain or maternal uterus. Learn about the causes and other types of cyst in the brain.
The main types of cyst in the head are:
1. Arachnoid cyst
The arachnoid cyst may be congenital, that is, it may be present in the newborn, called the primary cyst, or it may be due to infection or trauma and is called a secondary cyst. This type of cyst is usually asymptomatic and is characterized by accumulation of fluid between the membranes covering the brain. However, depending on its size, it can cause some symptoms, such as fainting, dizziness or balance problems. Learn about the symptoms, causes and treatment of arachnoid cyst.
2. Vascular plexus cyst
Vascular plexus cyst is rare, occurring in only 1% of fetuses, and is characterized by fluid accumulation in a brain cavity, usually in a region of the brain where there is dead tissue. This type of cyst can be diagnosed by ultrasound from the 14th week of gestation and does not require therapy, only follow-up, since it poses no risk to either the baby or the mother. Normally it is reabsorbed by the body itself after the 28th week of gestation.
3. Epidermoid cyst and dermoid
The epidermoid and dermoid cyst are similar, and are also the result of changes during the development of the fetus, but may also arise throughout life. They are a skin cyst that can appear on any part of the body, including the head, especially on the forehead and behind the ears. They are characterized by the accumulation of cells in the skin, do not cause symptoms and are free, that is, they can move on the skin.
The diagnosis is made from the evaluation of the characteristics of the cyst, such as size, if there is swelling and if the cysts are free. Treatment can be done by draining the liquid present in the cyst, with antibiotics, to avoid possible infections, or by surgery according to the medical recommendation.

Main symptoms of cyst in the head
Cysts in the head are usually asymptomatic, but cysts in the brain may cause some symptoms if they increase in size, such as:
- Headache;
- Nipple;
- Dizziness;
- Balance problems;
- Mental confusion;
- Seizures;
- Somnolence.
The diagnosis of the cysts in the head is made by a neurologist, in the case of the cysts of the brain, by means of computed tomography, magnetic resonance or ultrasonography or by the dermatologist by means of a physical examination, in the case of a cyst of skin, such as cyst epidermoid.
How to treat
Once a cyst is identified in the head, periodic follow-up with the neurologist should be initiated to monitor the size of the cyst, as well as the observation of the onset of symptoms.
If any symptom is observed, the doctor may indicate the use of some analgesic or remedies for dizziness or nausea. But if there is an increase in cyst size and persistence or increase in the frequency of symptoms, surgery may be indicated by the physician.