Viral pneumonia is an infection of the lung, which inflames the fine tissues responsible for breathing and generates symptoms such as high fever, shortness of breath and coughing with catarrh. This pneumonia occurs more in people with weakened immune systems, so it is more common in children and the elderly.
The main viruses causing this type of pneumonia are viruses that cause colds and flu, such as Haemophilus influenzae A or B, especially the most aggressive viruses such as H1N1 and H5N1, as well as others such as parainfluenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus and adenovirus, which can be carried in droplets of saliva from one infected person to another.
Thus, the virus of viral pneumonia is transmissible, however, it rarely causes pneumonia, being more common only the emergence of colds and flu, once the immune system is able to fight these microorganisms. Preventing the development of this pneumonia can be done by avoiding close contact with people with this infection, as well as having hygiene habits, such as keeping hands washed and sanitized.
How to know if it is viral pneumonia
Symptoms of viral pneumonia include:
- Dry cough, which evolves to cough with transparent, white or pink phlegm;
- Chest pain and shortness of breath;
- High fever, up to 39ºC;
- Sore throat or ear;
- Rhinitis or conjunctivitis, which may accompany the symptoms.
Viral pneumonia differs from bacterial pneumonia by generally having a more sudden onset, producing a more transparent or white phlegm, as well as having other signs of viral infection, such as nasal congestion, sinusitis, eye irritation and sneezing, however, it can be difficult to differentiate the 2 types of infection without doing any tests.
In the elderly, symptoms of pneumonia can also include confusion, extreme tiredness and lack of appetite, even if there is no fever. In infants or children, it is also very common to have very rapid breathing that causes the exaggerated opening of the wings of the nose. See other symptoms may indicate childhood pneumonia.
How to confirm the diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis of this disease, the doctor may order samples of respiratory secretions from the nose and throat for analysis in the laboratory, which should ideally be collected by the 3rd day of the disease, but can be collected by the 7th day after symptoms to identify the virus.
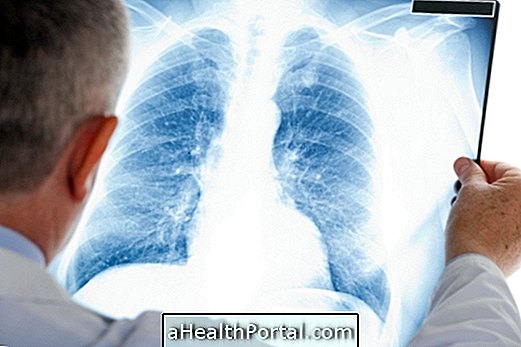
In addition, tests such as chest x-ray are performed to assess lung involvement and blood tests such as blood count, kidney function, and blood oxygenation to assess the degree and severity of the infection.
In any case of suspected pneumonia it is advisable to go through an appointment with the general practitioner or pulmonologist, or go to the emergency room, to start the appropriate treatment and avoid aggravation of the disease.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment for viral infections is doctor-oriented, and should be done with some guidelines such as:
- Rest at home, avoiding going to school or work;
- Good hydration, with water, tea, coconut water or natural juice;
- Light diet, avoiding fatty foods.
In addition, treatment of viral pneumonia or a flu virus caused by H1N1 or H5N1 viruses in people at increased risk of developing pneumonia, such as the elderly and children, also involves the use of antiviral drugs prescribed by the general practitioner or pulmonologist such as Oseltamivir, Zanamivir and Ribavirin, for example.
Treatment can be done at home. However, when the person shows signs of seriousness, such as difficulty breathing, low blood oxygenation, mental confusion or changes in the functioning of the kidneys, for example, hospitalization may be necessary for the vein and use of oxygen mask. Learn more about how viral pneumonia treatment should be treated.
In cases where viral pneumonia is contaminated by bacteria, or when it occurs in conjunction with bacterial pneumonia, the use of antibiotics such as Amoxicillin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin or Ceftriaxone is also indicated, for example, for about 7 to 10 days.
How to prevent
To prevent viral infections of any kind, it is very important to keep your hands clean, washing or using alcohol gel, whenever you go to public places, with buses, malls and markets, and avoid sharing personal objects such as cutlery and glasses .
The annual flu vaccine is also an important way to avoid infection with major types of virus.





-o-que--sintomas-e-tratamento.jpg)