Urethritis is an inflammation in the urethra that can be caused by internal or external trauma or by infection with some type of bacteria that can affect both men and women.
There are 2 main types of urethritis:
- Gonococcal urethritis : arises from infection with the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae, responsible for gonorrhea and, therefore, there is a risk of also having gonorrhea;
- Non-Gonococcal Urethritis : is caused by infection by other bacteria, such as Chlamydia trachomatis or E. coli, for example.
Depending on your cause, the symptoms may vary and, similarly, the treatment should also be done differently to ensure healing. Thus, whenever symptoms of urinary problems arise, consult the gynecologist or urologist to start the appropriate treatment.

Main symptoms
Symptoms of gonococcal urethritis include:
- Yellowish-green discharge, in great quantity, purulent and with bad smell coming from the urethra;
- Difficulty and burning in urination;
- Willingness to urinate frequently with too little urine.
Symptoms of non-gonococcal urethritis include:
- Little whitish discharge, which accumulates after urination;
- Burning on urination;
- Itching in the urethra;
- Discreet difficulty in urinating.
Usually non-gonococcal urethritis is asymptomatic, that is, it generates no symptoms.
See other common causes of pain when urinating and itching of the penis.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of urethritis can be made by the urologist or gynecologist by observing the symptoms that the individual presents and the analysis of the secretions that should be sent for laboratory analysis. It is recommended to start treatment before the test results, based on the symptoms presented.
Diagnosis of urethritis
The diagnosis of urethritis can be made by the urologist or gynecologist through observation of the symptoms and analysis of the secretions that should be sent for laboratory analysis. In most cases, the doctor may advise to start treatment even before the test results, based on the symptoms presented.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for urethritis should be performed with the use of antibiotic medicines; however, the antibiotic varies according to the type of urethritis:
In the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis, it is usually used:
- Azithromycin : single dose of 1 tablet of 1 g or Doxycycline : 100 mg, oral, 2 times daily, for 7 days.
In order to treat gonococcal urethritis, the use of:
- Ceftriaxone: 250 mg by single dose intramuscular injection.
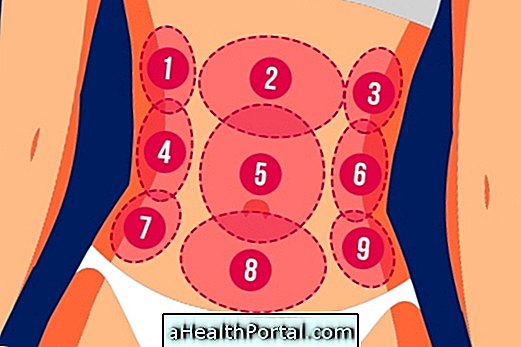
Urethral symptoms can often be confused with those of another problem called Urethral Syndrome, which is an inflammation of the urethra, which causes symptoms such as abdominal pain, urinary urgency, pain and irritation when urinating, and feeling of pressure in the abdomen.
Possible causes
The causes of urethritis can be:
- Internal trauma: may occur when using a bladder catheter to remove urine, as in the case of people hospitalized in a hospital.
- Infection by bacteria such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum , HSV or adenovirus.
Infectious urethritis is transmitted by unprotected intimate contact or by migration of bacteria from the intestines, in which case women are more prone to close proximity between the anus and the urethra.