Treatment of menstrual bleeding can be done with medications such as oral contraceptives, IUD use, and iron and folic acid intake.
However, in addition to these options, there are some simple cares with food that can help lessen discomfort and improve the woman's well-being.
In the most severe cases of menorrhagia, when the woman has already lost a lot of blood, she can be admitted to a blood transfusion to receive packed red blood cells and evaluate the possibility of surgery. When the cause is cancer, you can consider withdrawing the uterus.

Remedies for menstrual bleeding
The remedies that the gynecologist can indicate for the control of the menstrual bleeding can be:
- Oral contraceptives or IUDs - an intrauterine device to try to regulate menstruation and decrease blood flow;
- Iron supplements + folic acid to ensure the daily requirement of iron in the body, preventing or fighting anemia;
- Hemostatics, such as aminocaproic acid, to balance the consistency of blood.
Contraceptives can be changed after 3 months of use if they do not decrease menstrual flow.
When the blood test is normal, the doctor can only tell the woman about her condition and ask for ultrasound tests to try to identify the cause of the hemorrhage.
Medical treatment
If the remedies are not sufficient to stop heavy menstruation, the gynecologist may indicate curettage, intra-uterine Foley catheter, or laparoscopy or embolization of the uterine arteries.
If this cause is not found, but prolonged and prolonged menstruation, it is important to take care of food, consuming more iron, to prevent anemia, which may arise.

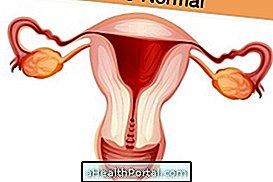
Surgery to remove the uterus
Surgery to remove the uterus may be indicated for women who can not stop menstrual bleeding even if they follow all medical guidelines and do not wish to become pregnant, so this should be the last treatment option.
Learn more about removal of the uterus.
Caring for food
Such care should be followed daily until complete resolution of menstrual bleeding that can last for many days or even months. Therefore it is recommended:
1. Drinking more fluids
Taking 2 to 3 liters of water or unsweetened tea per day is important not to get dehydrated. Pure, unsweetened orange juice is particularly indicated and can be taken 3 to 4 times a day because it contains minerals that can help keep blood pressure under control, avoiding the feeling of dizziness or fainting.
2. Eat more iron
Increasing consumption of iron-rich foods such as red meats, beans and beets is necessary to combat anemia that is already in place or prevent it from settling. Foods containing iron should be consumed daily, if possible at all meals to prevent too much iron levels in the blood.
Some rich iron recipes are citrus juice whipped with parsley, orange juice, carrot and beet, and the beetroot stewed. See more foods indicated in: Food rich in iron.
Signs of improvement
Signs of improvement in menstrual bleeding include a decrease in the amount of blood lost to the vagina, menstruation without clots, and the absence or decrease of the severity of the anemia. These signs of improvement may occur after 1 to 3 months from the start of treatment.
Signs of worsening
Signs of worsening may occur if the treatment is not performed correctly, in which case the bleeding may become even more intense or blood clots, worsening anemia. In this case, the woman may become very pale, lacking strength and having difficulty concentrating. When presenting these symptoms the doctor can request a hemogram to verify the amount of iron in the body, and to evaluate the possibility of hospitalization.
Complications that may arise
The complication that prolonged bleeding can cause is the development of anemia due to iron deficiency. However, when it is caused by serious changes like cancer, it can endanger the woman's life.