Leukorrhea is the name given to vaginal discharge, which may be chronic or acute, and may also cause itching and genital irritation. Its treatment is done with the use of antibiotics or antifungals in single dose or during 7 or 10 days depending on each situation.
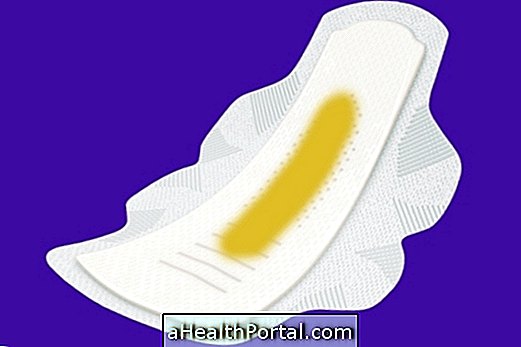
The physiological vaginal secretion, considered normal is transparent or slightly whitish, but when there are viruses, fungi or bacteria, in the female genital region, the vaginal secretion becomes yellowish, greenish or grayish.
Vaginal discharge or discharge can be caused by various diseases of the reproductive tract, such as inflammation of the ovary or uterus, candidiasis or even a simple allergy, so a well-done diagnosis is the ideal method to identify and treat your cause efficiently .
How to identify
The gynecologist is the doctor indicated to evaluate the vaginal discharge, it can make the diagnosis when observing the genital organ, the panties, when evaluating the pH of the vagina and if necessary can request the papanicolau for further clarification.
Usually the color, thickness and other symptoms present help the doctor identify which microorganism is involved and which treatment is appropriate in each case. Know what each color of vaginal discharge means and how your treatment is done.
Treatment for leukorrhea
Your treatment can be done with the use of antifungal medicines or antibiotics prescribed by the gynecologist, such as:
- 150 mg Fluconazole per week for 1 to 12 weeks;
- 2g of Metronidazole in single dose or 2 tablets of 500 mg for 7 consecutive days;
- 1g of azithromycin in single dose or
- 1g Ciprofloxacin in a single dose.
Infections can be caused by unprotected intimate contact and so treatment partners are recommended for treatment to achieve results.