The presence of peeling on the feet, which makes it look like they are peeling, usually happens when the skin is very dry, especially in people who do not moisturize the skin in that region or who wear flip-flops, for example. However, the peeling foot can also be a sign of some skin problems, such as infections, eczema or even psoriasis.
Thus, the ideal is that, if the peeling is very intense, it does not improve after hydrating the foot or if it appears associated with other symptoms such as pain, itching, redness or swelling, consult a dermatologist or general practitioner to identify the possible cause and start the most appropriate treatment.
The 5 main causes for the foot to be peeling are:
1. Dry skin
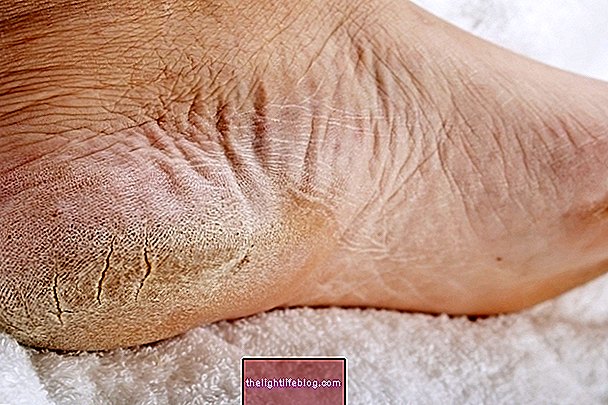
The foot is one of the parts of the body where the skin has an easier time to stay dry and, therefore, it is possible that flaking occurs, since the dead and dry skin cells are being released throughout the day.
This all happens because the foot needs to withstand the pressure of the body's weight, which causes the blood circulation to happen more slowly and the skin is not properly hydrated. Peeling from dry skin can also be aggravated in people who stand for a long time, who wear tight shoes, who often walk in flip-flops or who wear a lot of high heels.
What to do: the best way to moisturize your skin is to apply a moisturizing cream on your feet every day after bathing, for example, as well as drinking the recommended amount of water daily. In addition, avoiding the frequent use of tight shoes, flip flops and high heels also helps to relieve pressure on the foot, facilitating blood circulation and decreasing the chances of the skin becoming dry and peeling. Check out a ritual for taking care of dry feet at home.
2. Burn
Another very common cause for peeling feet is sunburn, especially sunburn. This is because most people forget to put sunscreen on their feet and then go out in the street wearing slippers, which makes the sun's rays easily burn the skin on their feet.
Another common situation for the appearance of burns on the feet is to walk barefoot on the sand or on a very hot floor, which has been in the sun for several hours, for example. When the foot gets burnt, it may be red and slightly sore, but a few days later it ends up peeling off.
What to do: to treat the burn it is important to cool the skin, especially in the first hours when it appears. For this you can dip your foot in a basin with cold water for 10 to 15 minutes or apply cold compresses of chamomile tea, for example. It is also important to apply moisturizer every day to reduce the chances of peeling. See what to do to take care of the burn.
3. Athlete's foot or ringworm
Athlete's foot, or ringworm, happens when there is a fungal infection in the foot, which is a relatively frequent situation, since the foot is a region that perspires a lot during the day.
This type of skin infection is more common in people who wear closed shoes, since in addition to sweating, the foot is also hot, which facilitates the development of fungi. Another way to catch athlete's foot is to walk barefoot in public places, such as swimming pools or changing rooms, for example.
The development of fungi on the skin has a tendency to cause intense peeling, in addition to other characteristic symptoms such as itching and stench. Check out the main symptoms of ringworm on the foot.
What to do: to treat yeast infection it is very important to keep your skin always clean and dry, so it is recommended to dry your foot very well after bathing, especially between the toes. Walking barefoot at home also allows you to aerate your skin and prevent fungi from continuing to develop. However, if symptoms do not improve, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist or general practitioner as it may be necessary to use antifungal ointments.
4. Eczema
Eczema is a common skin problem that causes excessive inflammation, resulting in itching, redness and peeling of the skin. Eczema usually appears when in contact with some type of specific material, such as synthetic fabrics or enamel, for example, but it can also arise from the use of some medication or for no apparent reason.
Symptoms of eczema usually appear for periods of greater intensity that are then relieved and may return again a few days or months later. Better understand what eczema is and how to identify it.
What to do: In some cases, eczema can disappear in a few hours or days, depending on the cause. However, when symptoms are persistent, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist, to identify the cause, assess the intensity of the symptoms and start treatment with anti-inflammatories and / or corticosteroids.
5. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is another relatively common skin disease that is characterized by the appearance of red patches on the skin that peel off and may not itch. These plaques can appear in various places on the body or affect only one part, such as elbows, scalp or feet.
Psoriasis is a chronic disease caused by the person's own immune system and, therefore, it is common to appear several times throughout life, especially when you are more stressed, when you have some type of infection or during the winter, for example .
What to do: in case of suspected psoriasis it is very important to consult a dermatologist because, although psoriasis has no cure, there are treatments that help to reduce symptoms such as the use of corticoid ointments, phototherapy or the use of immunosuppressive remedies. Learn more about psoriasis and how it is treated.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- STATPEARLS. Sunburn. 2020. Available at:. Accessed on Sep 23, 2020
- AM J CLIN DERMATOL. Management of acute sunburn. 2004. Available at:. Accessed on Sep 23, 2020
- NHS. Sunburn. Available in: . Accessed on Sep 23, 2020
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF MEDICINE AND FAMILY AND COMMUNITY HEALTH. Eczema: NHG M37 guideline summary. 2014. Available at:. Accessed on 15 Oct 2020
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF DERMATOLOGY. Eczema. Available in: . Accessed on 15 Oct 2020
- JUNIOR, Walter Belda et. al .. Dermatology Treaty. 2.ed. São Paulo: Atheneu, 2014. 145-170.
- LONGO, Dan L. et al .. Harrison Internal Medicine. 18.ed. São Paulo: AMGH Editora, 2013. 398-399.
- NATIONAL PSORIASIS FOUNDATION. About psoriasis. Available in: . Accessed on 30 Oct 2019
- NHS. Psoriasis. Available in: . Accessed on 30 Oct 2019