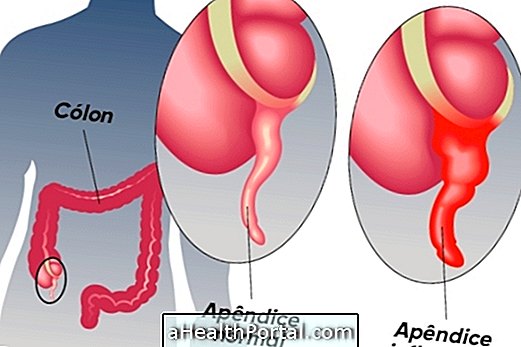
Appendicitis causes pain in the right side and under the abdomen, as well as low fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and feeling sick. Appendicitis can be caused by numerous factors, but the most common is the entry of a small amount of feces into the organ, leading to infection of the same.
Although the causes of appendicitis are not fully understood, some possible causes of appendicitis are:
- Accumulation of feces within the appendix, which can happen to any individual, of any age;
- Stone in the gallbladder, which can block the outflow of mucus;
- Pressure of the lymph nodes exerted on the appendix due to some infection;
- Appendix rupture due to local trauma, such as severe throbbing in the belly and car accidents;
- Intestinal parasite : A worm can enter the appendix and prevent the mucus from being produced by it, leading to an increase of the organ and its consequent rupture;
- Accumulation of gases within the appendix, which are produced by the bacteria that normally live there.
The appendix is an organ of the digestive system that is located between the large and small intestine and has the function of producing mucus constantly that mixes with the feces. But because it is an organ that has the shape of a gloved finger, whenever there is obstruction of the appendix the organ inflames generating appendicitis.
Which doctor to look for
If the individual suspects appendicitis, it is best to go to the emergency room as soon as possible to avoid organ rupture and its consequences.
Answer these questions and find out if you really can have an appendicitis: Symptoms of appendicitis.
How the Diagnosis is done
The diagnosis of appendicitis is made by observing the pain characteristic of the individual and by analyzing diagnostic exams such as magnetic resonance imaging, x-ray of the abdomen, simple examination of urine, blood, and feces.
These tests serve to exclude the hypotheses of other diseases and serve to confirm the inflammation of the appendix. If even the doctor remains in doubt, laparoscopy will be able to confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis.
As soon as the diagnosis is given, the doctor should indicate the removal of the appendix by surgery. This procedure prevents reinfections of the organ and reduces the risk of death due to complications of appendicitis, such as the entry of harmful bacteria into the body into the abdominal cavity and into the bloodstream.
What are the treatments for appendicitis?

Treatment for acute appendicitis
The treatment for acute appendicitis is done with surgery for the removal of the appendix, called appendectomy.
Surgery should be performed as soon as possible to avoid a new inflammation and the appendix breaks because if it ruptures it can lead to complications such as sepsis which is a serious infection of the body that can lead to death.
Currently, the most common surgical technique used to remove the appendix is laparoscopy, in which 3 small holes are made, allowing a quicker and less painful recovery. However, one can resort to traditional surgery by cutting the right region of the abdomen for removal of the appendix.
The hospitalization lasts about 1 to 2 days, recovery usually occurs around 15 days after surgery, and can reach 30 days in the case of traditional appendectomy and return to physical activities after 3 months.
In the first few days after surgery, the person should rest, eat foods high in fiber, avoid lifting heavy objects, drink plenty of fluids and avoid driving. Check out more details of what to eat after an appendicitis.
Treatment for chronic appendicitis
The treatment of chronic appendicitis is done with the use of analgesics, antipyretics, antibiotics and anti-inflammatories. However, it is possible that the medications are not enough and the individual has to undergo surgery to remove the appendix.