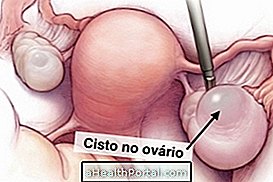
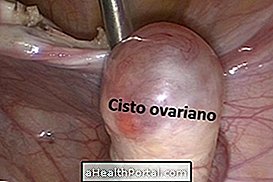
Ovarian cyst, also known as an ovarian cyst, is a fluid-filled pouch that forms in or around the ovary, which can cause pain in the pelvic region, delayed menstruation, or difficulty in getting pregnant.
Generally, the cyst in the ovary is benign and disappears after a few months without needing treatment, however, if you present symptoms, you may need medical treatment. See the symptoms here.
Having a cyst in the ovary is usually not serious because it is a common situation that occurs in many women between 15 and 35 years of age, and can occur several times throughout life.
Is it possible to get pregnant with an ovarian cyst?
Cyst in the ovary does not cause infertility, but the woman may find it difficult to get pregnant due to the hormonal changes that led to the cyst. However, with proper treatment, the cyst in the ovary tends to diminish or disappear, causing the woman to return to her normal hormonal rhythm, facilitating fertilization.
When a woman with an ovarian cyst can become pregnant, she should have regular visits to the obstetrician because there is a greater risk of complications, such as ectopic pregnancy.
Types of ovarian cysts
The main types of ovarian cysts include:
- Follicular cyst: it is formed when there is no ovulation or when the ovum does not leave the ovary during the fertile period. It usually has no symptoms and does not require treatment. Its size can vary from 2.5 cm to 10 cm and usually decreases in size between 4 to 8 weeks because it is not considered cancer.
- Corpus luteum corpus: may arise after the release of the egg and usually disappears without treatment. Its size varies between 3 and 4 cm and may rupture during intimate contact, but no specific treatment is necessary, but if there is severe pain, pressure drop and accelerated heartbeat, it may be necessary to withdraw through laparoscopic surgery.
- Teca-lutein cyst: It happens rarely, being more common in women who take medicines to get pregnant.
- Hemorrhagic cyst: it happens when there is bleeding in the wall of the cyst to its interior, being able to cause pelvic pain;
- Dermoid cyst: also called mature cystic teratoma, which can be found in the child, containing hair, tooth or bone fragment, requiring laparoscopy;
- Ovarian fibroma: it is a more common neoplasm in menopause, the size can vary from microcysts until weighing up to 23 kg, and must be removed by surgery.
- Ovarian endometrioma: arises in cases of endometriosis in the ovaries, needing to be treated with medicines or surgery;
- Adenoma cyst : benign ovarian cyst, which must be removed through laparoscopy.
Because they are filled with fluid, these cysts can still be known as anechoic cysts because they do not reflect the ultrasound used in diagnostic tests, however, the term anechoic is not related to severity.
The type of cyst in the ovary can be evaluated in the gynecologist through examinations such as ultrasound, laparoscopy or blood tests. Analgesics such as Dipirone can be used in case of pain, oral contraceptives can be used to suppress ovulation, which usually decreases follicular cysts, which are the most common. Placing a warm compress over the painful region may also relieve the discomfort, but whenever the pain is very intense you should go to the doctor or emergency room to perform a new ultrasound in order to observe if there was a growth or rupture of the cyst, assessing the need to have surgery.
What are the symptoms of cyst in the ovary?
Rarely a cyst on the ovary causes symptoms, but when it is very large, more than 3 cm in diameter, symptoms such as:
- Pain in the ovary, on the side where the cyst is;
- Pain during ovulation;
- Pain during intimate contact;
- Delay of menstruation;
- Increased breast tenderness;
- Vaginal bleeding outside the menstrual period;
- Weight gain because hormonal changes get fat;
- Difficulty getting pregnant.
The diagnosis of ovarian cyst can be made through examinations such as palpation of the pelvic region, transvaginal ultrasonography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. See the difference and know how to identify the symptoms of polycystic ovary.
The gynecologist can also ask for the pregnancy test because it values the Beta HCG to exclude the possibility of ectopic pregnancy, which presents the same symptoms, and even helps to identify the type of cyst that the woman possesses.
After identification of the cyst in the ovary the gynecologist may also request blood tests, such as the CA 125 whose maximum value should be 35 mUL, to check if the cyst is malignant and is considered an ovarian cancer.
Warning Signs
Warning signs that may indicate a possible twisting of the ovary, necessitating urgent surgery are:
- Intense pain on one side of the abdomen, which can relieve with hot compresses;
- Symptoms such as nausea and vomiting usually appear, which can be confused with appendicitis or bowel obstruction.
If the woman experiences these symptoms she should go to the emergency room as soon as possible.
Cysts that are more likely to break or twist are those that measure more than 8 cm. In addition, the woman who can get pregnant with a large cyst has a greater chance of twisting between 10 and 12 weeks because the growth of the uterus can push the ovary, with twisting.
Is cyst in the ovary cancer?
An ovarian cyst is usually not cancer, and is only a benign lesion that may disappear on its own or be removed through surgery, when it is too large, with a risk of disruption, or causes significant pain and discomfort. Ovarian cancer is more common in women over the age of 50, being very rare under 30.
Some characteristics of cysts that may be cancer are those with large size, with thick septum, solid area. In case of suspicion the doctor should request the CA 125 blood test, because this high value may indicate a carcinogenic lesion, however women with ovarian endometrioma may have elevated CA 125, not cancer.
Treatment for ovarian cyst
Having a cyst on the ovary is not always dangerous, and usually the treatment is to expect it to decrease in size alone, without the need for treatment.
However, ovarian cyst can also be treated by taking the contraceptive pill appropriate to each case, and when it causes symptoms or hinders the functioning of the organ, surgery can be recommended to remove the cyst without removing the ovary. In more severe cases, where the cyst is very large, has signs of cancer or in case of torsion of the ovary, it may be necessary to completely withdraw the ovary.
Natural treatment for ovarian cyst
Learn about a natural way to treat the cyst in the following video:

See also: Home Remedy for Ovarian Cyst