Glottal edema, known scientifically as laryngeal angioedema, is one of the symptoms that can occur in case of a severe allergic reaction, characterized by swelling in the throat region.
This is considered a medical emergency because the swelling that affects the throat can obstruct the flow of air to the lungs, so what to do include:
- Call for medical help by calling SAMU 192;
- Ask if the person has any allergy medicine, so that he / she takes it while waiting for the help;
- Keep the person preferably lying down, with legs elevated, to facilitate blood circulation;
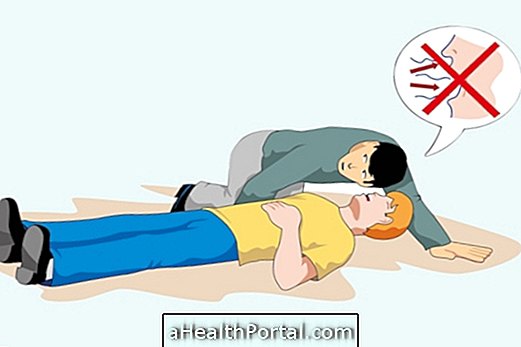
- Observing vital signs of the person, such as heartbeat and breathing, if they are absent, will require cardiopulmonary resuscitation, with cardiac massage. Check out the step-by-step of what to do in case of a cardiorespiratory arrest.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction appear quickly after a few minutes of exposure to the allergy substance, including difficulty breathing, sore throat, or wheezing when breathing.
The signs and organs affected will depend on the reaction of each person's immune system and, in addition to glottal edema, other dangerous allergy reactions that may be fatal are the asthma attack and anaphylactic shock. If you want to know more about how a severe allergic reaction happens, check out Anaphylactic Shock.

Symptoms of glottis edema
The symptoms of glottal edema are:
- Sore throat sensation;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Wheezing or a rattling noise during breathing;
- Hoarseness;
- Difficulty talking.
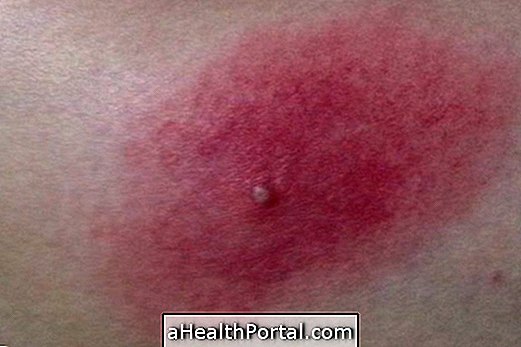
There are other symptoms that usually accompany glottal edema and are associated with allergy, such as hives, redness or itching of the skin, swollen eyes and lips, enlarged tongue, itchy throat, conjunctivitis or asthma attack, for example.
These symptoms usually appear in 5 minutes to 30 minutes after exposure to a substance that causes allergy, which may be a medicine, a food, an insect bite, temperature changes or even a genetic predisposition, in people with a disease called Hereditary angioedema. Learn more about this disease here.
How is the treatment done?
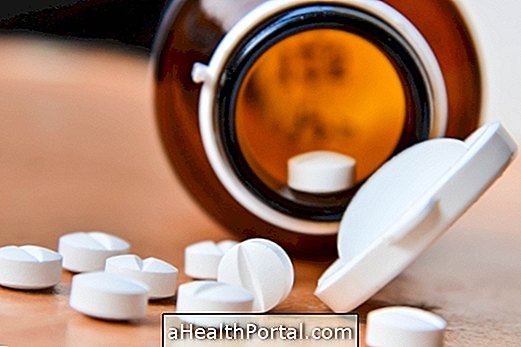
After evaluation of the medical team and confirmation of the risk of glottal edema, treatment is indicated, with medications that will rapidly decrease the action of the immune system, and include the application of injections containing adrenaline, antiallergics and corticosteroids.
Because there may be an intense difficulty breathing, it may be necessary to use an oxygen mask or even an orotracheal intubation, where a tube is placed through the person's throat so that their breath is not blocked by swelling.