Shigellosis, also known as bacterial dysentery, is an infection of the intestine caused by the Shigella bacteria, which causes symptoms such as diarrhea, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting and headache.
This infection usually occurs through ingestion of water or food contaminated by faeces and is therefore more frequent in children who do not wash their hands after playing on grass or sand, for example.
Typically, shigellosis disappears naturally after 5 to 7 days, but if symptoms persist or worsen it is advised to go to the general practitioner to confirm the diagnosis and initiate treatment if necessary.

Signs and symptoms
The first symptoms of Shigella infection appear 1 to 2 days after contamination and include:
- Diarrhea, which may contain blood;
- Fever above 38ºC;
- Bellyache;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Willingness to defecate constantly.
However, there are also people who have the infection but do not have symptoms and so the body can eliminate the bacteria without knowing that they have ever been infected.
These symptoms may be more intense in people who have weakened immune systems, such as in the case of the elderly, children or diseases such as HIV, cancer, lupus or multiple sclerosis, for example.
How to confirm the diagnosis
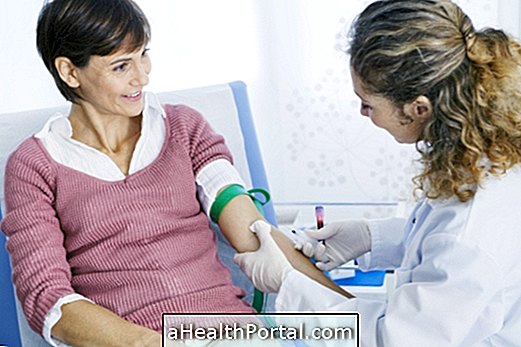
The only way to confirm the diagnosis of Shigellosis is to do a fecal examination to identify the presence of the Shigella bacteria in the laboratory .
However, in most cases, the doctor only identifies that you have a bowel infection, indicating the generic treatment for those cases. Only when the symptoms do not improve after 3 days can the doctor ask for stool testing to confirm the cause and start a more specific treatment.
How is the treatment done?
In most cases, shigellosis is treated naturally by the body because the immune system can eliminate the bacteria in about 5 to 7 days. However, to relieve symptoms and speed recovery are advised some care as:
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day, or whey, or coconut water;
- Keep at home for at least 1 or 2 days;
- Avoid remedies for diarrhea because they prevent the bacteria from being eliminated;
- Eat a light meal, with few fats or sugary foods. See what you can eat in a bowel infection.
When the symptoms are too intense or too slow to go away, the doctor may prescribe the use of an antibiotic, such as azithromycin, to help the body eliminate the bacteria and ensure healing.
When to go to the doctor
Although the treatment can be done at home, it is important to go to the doctor to start a more specific treatment when the symptoms worsen, do not improve after 2 or 3 days or when blood appears in the diarrhea.
How to prevent infection with shigellosis
The transmission of shigellosis occurs when food or objects contaminated with feces are placed in the mouth and, in order to avoid infection, one should take care of the day-to-day life, such as:
- Wash hands regularly, especially before eating or after using the toilet;
- Wash food before eating, especially fruits and vegetables;
- Avoid drinking water from lakes, rivers or waterfalls;
- Avoid close contact with people with diarrhea.
In addition, people who have this infection should also avoid preparing food for others.