The symptoms of Addison's disease may arise gradually, and it is usually characterized by increased urge to consume salt, excessive tiredness, muscle weakness, joint and muscle pain, and changes in skin pigmentation.
Addison's disease occurs when the adrenal or adrenal gland has changes in its function, leading to a decrease in the production of hormones. Treatment should be done throughout life, and the use of corticosteroids and hormone replacement therapy is usually indicated by the endocrinologist. Know the causes and treatment for Addison's disease.
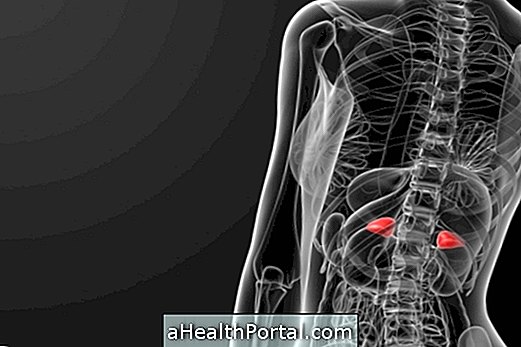
Main symptoms
The symptoms of Addison's disease usually arise gradually, depending on how the disease develops, but may also appear suddenly, the main ones being:
- Muscle weakness;
- Skin pigmentation changes that darken the hands, face, knees and elbows;
- Slimming without apparent cause;
- Loss of appetite;
- Gastrointestinal malaise such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea;
- Pressure drop upon standing up, feeling dizzy;
- Loss of hair:
- Abdominal pain;
- Excessive desire to eat salt, since there is a great loss of salt in the urine;
- Fever;
- Nausea;
- Fatigue;
- Muscle and joint pain;
- Alteration in the level of consciousness;
- Decreased libido;
- Alteration in the menstrual cycle in the case of women;
- Loss of body hair.
The treatment of Addison's disease is established by the endocrinologist according to the symptoms presented by the patient, and the treatment must be done throughout life, since this disease has no cure. Usually the use of corticosteroids and hormone therapy is indicated to balance the level of hormones in the body.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of Addison's disease is usually made in more advanced stages of the disease, as the adrenal glands usually wear out gradually and there are no symptoms at first.
The diagnosis is made by the endocrinologist through clinical examination, in which the symptoms presented by the patient are observed, followed by laboratory and imaging tests. The purpose of the requested blood test is to check the concentration of sodium and potassium in the blood, as well as to check the amount of circulating leukocytes and lymphocytes. In addition, the ACTH stimulation test can be performed, in which the concentration of cortisol is measured before and after the injection of synthetic ACTH.
Regarding the imaging tests, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may be ordered to evaluate the adrenal glands.
Differential diagnosis
The symptoms of Addison's disease can be confused with other diseases, so it is important that as many tests as possible that allow the differentiation of the different conditions are carried out. The differential diagnosis is usually made for pituitary tumors, as this type of tumor can lead to changes in the production of the ACTH hormone, which may result in symptoms similar to Addison's disease.
In addition to the pituitary tumors, a differential diagnosis is made for tuberculosis, pituitary sarcoidosis, vitiligo and chronic skin diseases, as they may also present with hyperpigmentation of some regions of the body.