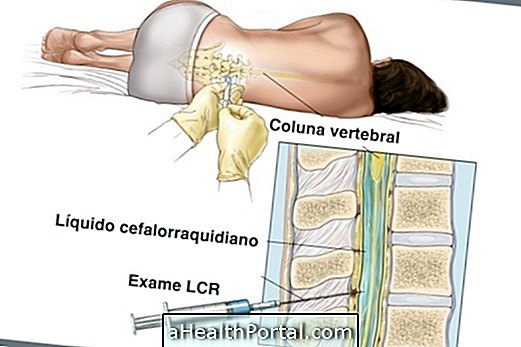
The child may be dengue when she has symptoms such as fever and lack of appetite, which are more worrisome in times of disease epidemic. However, dengue in children is not always accompanied by symptoms, so it is often only identified when you are already at a serious stage.
In general, children have the same signs of age-related illnesses as influenza, which can confuse parents. The diagnosis of dengue is done through a blood test that identifies the virus, and only when the disease is discovered early on, can the child be treated at home.
Symptoms of dengue in children
The child with dengue may not have symptoms or flu-like symptoms, so the disease often passes quickly into the severe stage without being noticed. In general, the symptoms are:
- Apathy and muscle weakness;
- Somnolence;
- Fever;
- Headache;
- Refusal of food and liquids;
- Vomiting;
- Diarrhea or loose stools;
- Bleeding in the nose or gums;
- Red spots on the skin.
In children younger than 2 years, symptoms such as headache and muscle pain can be identified by persistent crying and irritability. It is normal for a child not to have difficulty breathing, and parents end up confusing the dengue fever with common infections that babies have at that age.
Signs of dengue complication
The main signs of dengue complications in children appear between the 3rd and 7th day of illness when the fever passes. These signs are:
- Frequent vomiting;
- Severe abdominal pain that does not go away;
- Swollen belly;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Somnolence;
- Irritability;
- Delirium;
- Memory loss;
- Temperature less than 35 ° C.
In general, dengue fever in children worsens rapidly and the onset of these signs is a warning for the onset of severe disease. Thus, the pediatrician should be sought as soon as the first symptoms appear, so that the disease is identified before moving to the severe form.

Diagnosis of dengue fever
The diagnosis of dengue is done through a blood test to evaluate the presence of the virus. However, the result of this examination takes a few days, and the doctor starts treatment as soon as the signs of the disease are identified in the child.
Treatment of dengue
Treatment of dengue begins as soon as symptoms are identified, even without confirmation of the diagnosis by blood test. The type of treatment that will be used depends on the severity of the illness, and only in milder cases can the child be treated at home. In general, treatment includes:
- Ingestion of liquids;
- Serum through the vein;
- Medicines to control the symptoms of fever, pain and vomiting.
In more severe cases, the child needs to be admitted to the ICU. Usually dengue fever lasts for about 10 days, but full recovery can take anywhere from 2 to 4 weeks.
Because the child may have dengue more than once
All people, children and adults, may have dengue again, even if they have had the disease before. As there are 4 different viruses for dengue, the person who got dengue once is immune only to that virus, and can get even more 3 different types of dengue. In addition, it is common for people who have had dengue to develop dengue hemorrhagic fever, and so disease prevention care should be maintained. Learn how to make a homemade repellent in: dengue prevention.