In most cases, the lump behind the ear is not a sign of something dangerous, and may form due to various factors such as infections, sebaceous cysts or acne conditions, for example, requiring a simple treatment.
However, if the lump grows continuously, persists for a long time or causes a lot of discomfort, it may be necessary to resort to a more invasive treatment, such as a surgery, for example.

The lump behind the ear can have several origins:
1. Infection
Pimples behind the ear can be caused by infections in the throat or neck, such as pharyngitis, cold, flu, mononucleosis, ear infections, conjunctivitis, herpes, cavities, gingivitis and periodontitis, toxoplasmosis, tonsillitis, HIV or measles, for example.
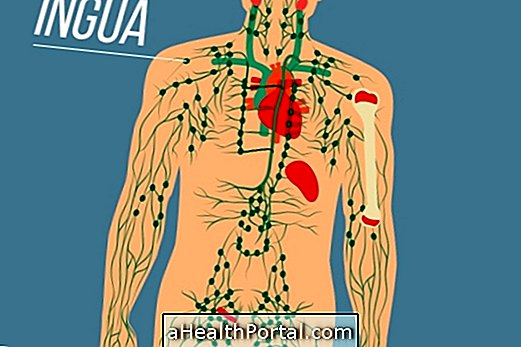
In addition, during an infection, an increase in the size of lymph nodes, which are located in various places of the body such as under the arms, behind the ears and in the neck, is also very frequent.
2. Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis consists of an infection in the bone behind the ear, which can occur after an ear infection, especially if it is not well treated, and may give rise to a lump. This problem may be accompanied by headache, decreased hearing ability and fluid release from the ear. Learn more about the symptoms and treatment of mastoiditis.
3. Acne
In acne, the pores of the skin can become blocked due to excess sebum production by the sebaceous gland, located at the base of the hair follicle, which mixes with skin cells, and this mixture forms a spine that can swell and become sore. Learn how to treat acne.
Sebaceous cyst
The sebaceous cyst is a type of lump that forms under the skin, which is composed of a substance called sebum, which can arise in any region of the body. It is usually soft to the touch, it can move when it is touched or pressed and does not normally hurt, unless it becomes inflamed, tender and reddish, making it painful and a dermatologist remove the cyst. See more about sebaceous cyst.
The lump on the skin, rounded and soft may also be a lipoma, a benign tumor type composed of fat cells, which should also be removed through surgery or liposuction.
5. Lipoma
Lipoma is a painless, non-malignant type of fat cell that can grow anywhere in the body and grows slowly. Learn how to identify lipoma.
What differentiates lipoma from a sebaceous cyst is its constitution. Lipoma is composed of adipose cells and the sebaceous cyst is composed of sebum, however, the treatment is always the same, and consists of surgery to remove the fibrous capsule.
6. Swelling of the lymph nodes
Lymph nodes, also known as gills, are scattered throughout the body, and when they become enlarged, usually indicate an infection or inflammation of the region in which they arise, and may also arise due to autoimmune diseases, use of medicines or even cancer of head, neck or lymphoma, for example. Understand the function of lymph nodes and where they are.
Generally, the anus usually have benign and transient causes, having a few millimeters in diameter and disappearing in a period of about 3 to 30 days. However, if they continue to grow, last longer than 30 days or are accompanied by weight loss and fever, it is important to see a doctor for proper treatment.
When to go to the doctor
You should go to the doctor if the lump behind the ear suddenly appears, remains fixed and still to the touch, persists for a long time, or if accompanied by signs and symptoms such as:
- Pain and redness;
- Increase in size;
- Shape change;
- Difficulty in moving the head or neck;
- Difficulty swallowing.
In these cases, the doctor may make a physical assessment of the lump based on its appearance and reaction to the touch, as well as an evaluation of other symptoms such as fever and chills, which may indicate infection. If the lump is sore, it may be an abscess or a spine.
The treatment depends largely on the origin of the stone and may disappear without any treatment, or it may consist of administration of antibiotics in case of infection or even surgery in the case of lipomas and sebaceous cysts.