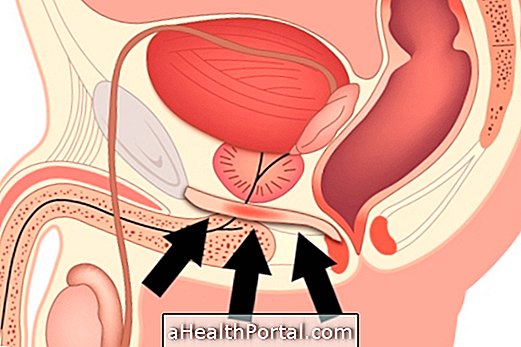
Chronic endometritis is a recurrent inflammation of the endometrium, the lining of the inner part of the uterus. It can be caused by sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis or chlamydia, pelvic inflammatory disease, salpingitis, injury and damage during labor or abortion, and by insertion of an intrauterine device.
This chronic inflammation can lead to infertility, miscarriages, failure to implant the embryo after fertilization and premature labor.
Treatment of chronic endometritis
Treatment of chronic endometritis may involve the use of oral or intravenous antibiotics. Resting and drinking lots of water are important complements for the treatment to be faster and with success.
Treatment for chronic endometritis should involve the partners in the relationship to reduce the risk of new infections. In more complicated cases, hospital admission is necessary.
Symptoms of chronic endometritis
Symptoms of chronic endometritis may include:
- General malaise;
- Fever;
- Pelvic pain;
- Vaginal bleeding;
- Vaginal discharge with smell and white or yellow color;
- Constipation;
- Belly growth.
Endometritis may be short, ie acute, and is characterized by hypogastric pain, high fever, painful menses and yellow vaginal discharge, and vaginal bleeding.
The diagnosis of endometritis consists of evaluating the symptoms presented by the woman and using complementary diagnostic tests such as blood tests, endometrial biopsy, laparoscopy and culture and analysis of bacteria.