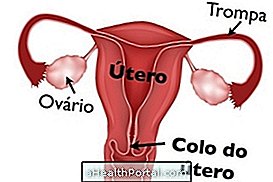
The wound in the cervix, scientifically called cervical or papillary ectopy, is caused by an inflammation of the cervix. Therefore, it has a variety of causes, such as allergies, product irritations, infections, and may even be a cause of hormone change throughout a woman's life, including childhood and pregnancy, and may occur in women of all ages .
It does not always cause symptoms, but the most common are discharge, colic and bleeding, and the treatment can be done with cauterization or with the use of medicines or ointments that help heal and fight infections. The wound in the uterus has healing, but if left untreated it can increase, and even turn, cancer.

What are the symptoms
Symptoms of wounds in the uterus are not always present, but can be:
- Residues in panties;
- Vaginal discharge of yellowish color, white or greenish;
- Colic or discomfort in the pelvic region;
- There may be itching and burning when you urinate;
- There may be vaginal bleeding after intercourse.
Diagnosis of the wound in the cervix can be done through pap smears or colposcopy, which is the examination in which the gynecologist can see the uterus and evaluate the size of the wound. In the virgin woman, the doctor can observe the discharge when analyzing the panties and through the use of a cotton swab in the region of the vulva, which should not break the hymen.
How to treat
Treatment for wounds in the uterus can be done with the use of gynecological creams, which are healing or hormone-based, to facilitate wound healing, which should be applied daily for the time determined by the doctor. Another option is the cauterization of the wound, which can be laser or with the use of chemicals. Read more in: How to treat the wound in the womb.
If it is caused by an infection such as candidiasis, chlamydia or herpes, for example, specific anti-microbial drugs such as antifungal, antibiotic and anti-viral drugs prescribed by the gynecologist should be used.
In addition, a woman who has a wound in the uterus has a greater risk of becoming infected with diseases, so she should take greater care, such as condom use and vaccination for HPV.
To identify a lesion as early as possible and reduce health risks, it is important that all women consult with a gynecologist at least once a year, and whenever there are symptoms such as discharge, seek medical help immediately.
Main causes
The causes of the cervical wound are not fully understood but may be linked to inflammation and untreated infections such as:
- Alterations of hormones in childhood, adolescence or menopause;
- Uterine changes in pregnancy;
- Injury after childbirth;
- Allergy to the products of the condom or internal absorbents;
- Infections such as HPV, Chlamydia, Candidiasis, Syphilis, Gonorrhea, Herpes.
The main way to get an infection from this region is through intimate contact with a contaminated individual, especially when the condom is not used. Having many intimate partners and not having proper intimate hygiene also facilitate the development of a wound.

Does wounding in uterus hinder getting pregnant?
The wound in the cervix can disrupt the woman who wants to become pregnant, because they alter the pH of the vagina and the sperm can not reach the uterus, or because the bacteria can reach the fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease. However, mild injuries usually do not interfere with pregnancy.
This disease can also happen during pregnancy, which is common due to hormone changes in this period and should be treated as soon as possible, as inflammation and infection can reach the inside of the uterus, amniotic fluid and baby, causing risk abortion, premature birth, and even infection of the baby, which can have complications such as delayed growth, difficulty breathing, changes in the eyes and ears.
Can Uterine Wound Cause Cancer?
The wound in the womb usually does not usually cause cancer, and is usually resolved with treatment. However, in cases of rapidly growing wounds, and when treatment is not performed properly, the risk of becoming cancer is increased.
In addition, the chance of a wound in the uterus turning cancer is greater when it is caused by the HPV virus. The cancer is confirmed through the biopsy performed by the gynecologist, and treatment should be started as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed, with surgery and chemotherapy.