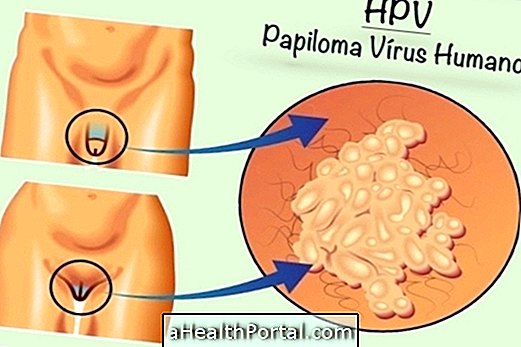
Some of the most common genital infections, both in men and women, include candidiasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, or syphilis, and to identify them you need to know how to recognize a symptom because each disease has its own symptoms.
Genital infections in women should be treated by a gynecologist and in the man by a urologist, and for their diagnosis the doctor will perform a blood test and a collection of the discharge, to effectively identify the type of infection present. The recommended treatment varies according to the type of infection and can be done using antibiotic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory or antiviral medicines.
How to identify the most common infections in women
To identify the most common genital infections in women, be aware of the following symptoms:
| Symptoms | What can it be | How to treat |
| Bleeding, itching, burning, swelling, redness and pain during intimate contact. | Candidiasis (Candida albicans) | Antifungals in tablets or ointment. Learn more about treatment here. |
| White, yellow, or green discharge with itching, itching, and pain in the intima | Trichomoniasis (Trichomonas vaginalis) | Antibiotics like Metronidazole |
| Thrush-like blisters in the intima region that cause itching and pain, painful urination, general malaise, and fever | Genital Herpes (Herpes Simplex) | Antivirals like Zovirax |
| Small wound in the intimate region, lumps in the neck with pain, headache, general malaise and fever | Syphilis (Treponema pallidum) | Antibiotics like Penicillin |
| Yellow or green discharge and thick, pain and burning while urinating, abdominal discomfort, vaginal bleeding especially after intimate contact | Gonorrhea (Neisseria gonorrhoeae) | Antibiotics such as Azithrocymin |
| Yellow discharge, pain when urinating in the lower part of the belly, pain and vaginal bleeding during intimate contact | Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis) | Antibiotics like Azithromycin |
| Abundant and thick discharge with bad smell, excessive discharge after intimate contact, itching and pain in the genital area | Bacterial vaginosis (Gardnerella vaginalis) | Antibiotics like Metronidazole. See how the treatment is done here. |
| Yellow, green or brown discharge with malodor, pain and bleeding during intimate contact and pain when urinating | Cervicitis | Antibiotics like Azithromycin. Learn more about treatment here. |

Some symptoms of genital infections in women are common, so the best way to know which genital infection a woman has is to see her gynecologist. During the consultation, the gynecologist will ask for an analysis of the vaginal discharge to know what disease is treated, as well as a general analysis of the symptoms manifested.
How to identify the most common infections in men
To identify the most common genital infections in man, one must be aware of the symptoms described in the following table:
| Symptoms | What can it be | How to treat |
| Pain and burning when urinating and in the testicles, yellow discharge, fever, swelling and redness in the opening of the penis | Gonorrhea (Neisseria gonorrhoeae) | Antibiotics like Azitrocymin. See how the treatment is here. |
| Pain when urinating, discharge, pain and swelling in the testicles | Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis) | Antibiotics like Azithromycin |
| Swelling and pain in the testicles, fever, nausea, vomiting, and blood in urine and semen | Orquite (C. trachomatis or N. gonorrheae) | Anti-inflammatory or Antibiotics |
| Redness, swelling and white plaques on the penis, discharge and pain and discomfort during intimate contact |
Candidiasis (Candida albicans) | Antifungals in tablets or ointment |
| Yellow, green, brown, or bloody discharge, pain and difficulty passing urine, swelling of the testicles, itching, and irritation at the tip of the penis | Urethritis (C. trachomatis or N. gonorrheae) | Antibiotics like Azithromycin |
| Thrush-like blisters in the intima region that cause itching and pain, painful urination, general malaise, and fever | Herpes (Herpes Simplex) | Antivirals like Zovirax. Learn more about treatment here. |
| Injured in the intimate region, lumps in the neck with pain, headache, general malaise and fever | Syphilis (Treponema pallidum) | Antibiotics like Penicillin |
| Swollen, sore, red and hot testicles, painful urination, urgency to urinate, nodules in the testicles, lumps with groin pain, runny, bloody semen and fever. | Epididymitis (C. trachomatis or N. gonorrheae) | Antibiotics like Ceftriaxone |

In the case of man, the best way to know what genital infection is present is to consult the urologist to take a sample of the discharge and have a blood test.
How to treat
The treatment of genital infections in both men and women should be doctor-directed and can be done using antibiotics, antifungal, anti-inflammatory and antiviral medicines, in the form of tablets or ointments, which depend on the type of micro-organism that is causing the infection . In most cases, as many of these diseases are sexually transmitted, the partner should also do the same treatment, even when there are no symptoms. In addition, throughout the treatment or until the disappearance of all the symptoms is recommended the use of condoms, to avoid new contagions with the disease.