Treatment of congenital syphilis is always recommended when the mother's syphilis treatment status is not known when treatment of the pregnant woman was only started in the third trimester or when the baby is difficult to follow after birth.
This is because all babies born to mothers infected with syphilis may show positive results on the examination of syphilis done at birth, even if they are not infected, due to the passage of antibodies from the mother through the placenta.
Thus, in addition to blood tests, it is also important to be aware of the symptoms of congenital syphilis that appear in the baby, to decide the best form of treatment. See what are the main symptoms of congenital syphilis.
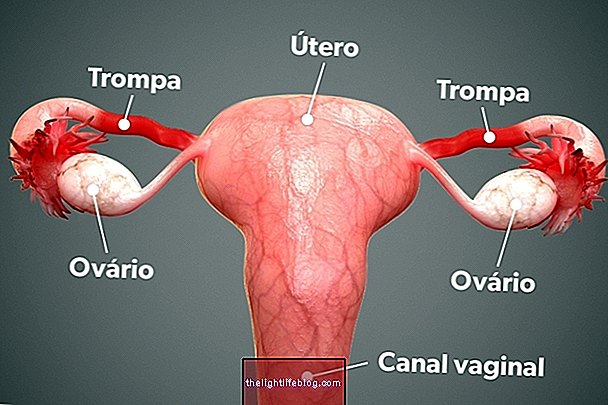
Treatment of syphilis in the baby

The treatment of the baby varies according to the risk of infection by syphilis:
1. Very high risk of having syphilis
This risk is determined when the pregnant woman has not been treated for syphilis, the physical examination of the baby is abnormal, or the baby's syphilis test has higher VDRL values than the mother. In these cases, the treatment is done in one of the following ways:
- Injection of 50, 000 IU / kg of crystalline aqueous penicillin every 12 hours for 7 days, followed by 50, 000 IU of crystalline aqueous penicillin every 8 hours between the 7th and 10th day;
- Injection of 50, 000 IU / kg of procaine Penicillin once daily for 10 days.
In any case, if more than one day of treatment fails, it is recommended to start the injections again, to eliminate the risk of not fighting the bacteria correctly or being infected again.
2. High risk of having syphilis
In this case, all the infants who have a normal physical examination and syphilis test with VDRL value equal to or less than that of the mother are included, but who were born to pregnant women who did not adequately treat syphilis or started treatment less than 4 weeks before childbirth
In these cases, in addition to the treatment options for babies at very high risk of syphilis, another option may be used, which consists of a single injection of 50, 000 IU / kg benzathine penicillin. However, this treatment can only be done if there is certainty that the physical examination does not have any change and the baby may be accompanied by the pediatrician to do regular examinations of syphilis.
3. Low risk of having syphilis
Babies at low risk of having syphilis have a normal physical examination, a syphilis test with VDRL value equal to or less than that of the mother, and the mother initiated appropriate treatment more than 4 weeks before delivery.
Usually, the treatment is done with a single injection of 50, 000 IU / kg benzathine penicillin, but the doctor may also choose not to inject and only keep track of the development of the baby with frequent syphilis tests.
4. Very low risk of having syphilis
In this case, the baby has a normal physical examination, a syphilis test with a VDRL value equal to or less than that of the mother, and the pregnant woman did the appropriate treatment before becoming pregnant, presenting low VDRL values throughout the pregnancy.
Usually, the treatment is not necessary for these babies and should only be accompanied with regular syphilis tests. If it is not possible to maintain frequent monitoring, your doctor may recommend a single injection of 50, 000 IU / kg benzathine penicillin.
Treatment of syphilis in pregnancy

During pregnancy, the woman should be tested for VDRL in the three quarters to check whether or not the bacteria are present in the body. A decrease in viral load does not mean that the disease has been cured and continued treatment is required until the end of pregnancy.
Performing the serological test for syphilis by removing blood sample from the umbilical cord is important to know whether or not the baby is already infected with the disease. Blood samples drawn from the baby at birth are also important in assessing whether or not he or she has been infected with syphilis.
Treatment of pregnant women during pregnancy occurs as follows:
- In primary syphilis: a total dose of 2, 400, 000 IU of benzathine penicillin;
- In secondary syphilis: total dose of 4, 800, 000 IU of benzathine penicillin;
- In tertiary syphilis: a total dose of 7, 200, 000 IU of benzathine penicillin;
In neurosyphilis it is recommended that 18 to 24 million IU per day of crystalline aqueous penicillin G be injected intravenously, divided into doses of 3-4 million U every 4 hours for 10 to 14 days.
Learn more about treatment, including how the treatment is done when the pregnant woman is allergic to Penicillin.