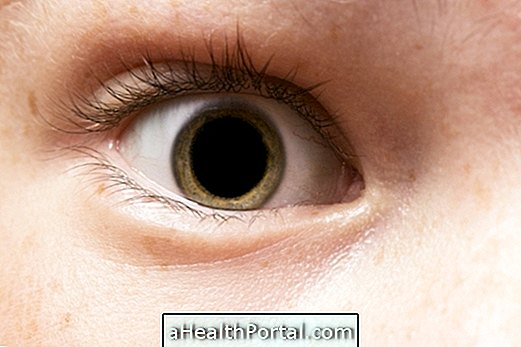
Every diabetic should pay special attention to the health of their eyes as the high concentrations of glucose in the blood can lead to various eye diseases. One of the most frequent complications of diabetes is diabetic retinopathy, an injury to the eye that can lead to permanent blindness. Other eye diseases caused by diabetes are: glaucoma and cataracts, which can also progress to blindness, although there are effective forms of treatment that can bring healing to the disease.
These complications develop more easily in people with type 1 diabetes, and glucose control and frequent monitoring of diabetics is the most efficient way to avoid these consequences. Learn how to control diabetes to avoid complications.
The main ocular complications caused by diabetes are:
1. Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy begins in a mild way, and in some cases it develops into the most severe form of the disease, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, where there is a great impairment of vision, and there may be haemorrhage, retinal detachment, formation of opaque membranes and neovascularization of iris.
Argon laser photocoagulation and vitrectomy are the best forms of treatment for proliferative diabetic retinopathy, but it should be clearly understood that the best way to prevent the progression of the disease to blindness is through daily control of blood sugar rates and the accomplishment of at least 1 annual consultation with the ophthalmologist.
Learn more about this disease in: Diabetic Retinopathy
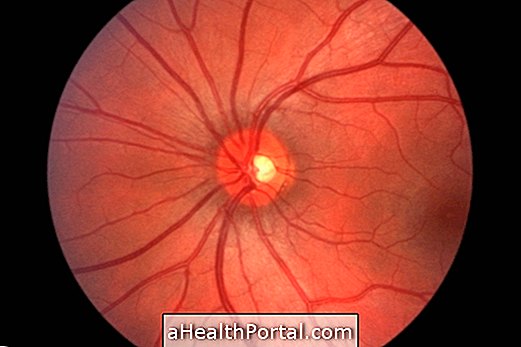
2. Glaucoma
Glaucoma is characterized by increased pressure inside the eye. Over time, this high pressure damages the optic nerve, which can lead to loss of the lateral view of your eye. Learn to identify the early symptoms of glaucoma.
Its treatment can be done with the daily use of eye drops to lower the pressure in the eye, but sometimes the ophthalmologist may indicate a laser surgery.
3. Cataract
The cataract is a kind of cloud that forms on the lens of the eye, which leaves the vision blurred, its treatment is the removal of this 'cloud' and the placement of a lens inside the eye. Learn more details of cataract surgery.
What to do in case of suspected visual change
If you have diabetes and note that you are having difficulty reading, you experience pain in the eyes, if they get red and if you feel dizzy at certain times of the day, you should measure your blood glucose daily to know that diabetes is properly controlled and follow the treatment indicated by the doctor to keep the blood sugar rate under control.
In addition, it is advisable to go to an appointment with an ophthalmologist to perform all the examinations necessary to identify any eye complications early. The best way to deal with this situation is by finding out what it is and initiating appropriate treatment because the complications of diabetes in the eyes may be irreversible and blindness is a possibility.
Even those who do not show any visual changes should go to the ophthalmologist once a year to perform tests that can identify possible changes as soon as they appear.