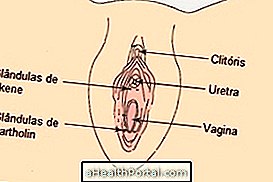
Skene's glands are located on the side of the woman's urethra, near the entrance of the vagina, as shown in the picture, and are responsible for releasing a fluid that represents female ejaculation during intimate contact.
Usually, Skene's glands are more developed in some women and so it may be more difficult to stimulate the gland in women who have them less developed.
In some cases, when the Skene's gland becomes clogged, fluid may accumulate inside it, causing inflammation and causing a cyst to appear that can be treated with anti-inflammatory drugs or surgery, for example.
Photos of the Skene gland
Inflammation of the Skene gland
The inflammation of the Skene gland can occur due to an obstruction of the gland channels, which causes the liquid instead of being released to accumulate in the gland, giving rise to the cyst of the Skene gland . The cyst usually does not show symptoms, however the region can become inflamed, swollen, reddish and sore.
In addition to inflammation, the cyst may become infected, giving rise to an abscess, which is a pus infection. In this case, and when the cyst is large, the woman may have fever, pain during intimate contact, while sitting, walking and urinating, sensation of a ball in the vagina and exit of pus, and may also develop urinary retention or a urinary tract infection .
Function of the Skene gland
The function of the Skene gland is to produce and expel a colorless or whitish, viscous fluid through the urethra during intimate contact when the glands are stimulated, giving rise to female ejaculation.
Ejaculated fluid is unrelated to vaginal lubrication, because lubrication occurs before orgasm and is produced by the Bartholin glands, while ejaculation occurs at the climax of intimate contact and the fluid is released through the urethral canal. Learn more about lubrication in: Bartholin's Gland.
Treatment for cyst in the Skene gland
The treatment for cyst in the Skene gland should be directed by a gynecologist, but is usually started with painkiller and anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibuprofen or Paracetamol, to relieve pain and reduce swelling.
In addition, if the cyst is infected, it may be necessary to take antibiotics such as Amoxicillin or to drain the cyst through a small surgical cut to drain the pus.
In more severe cases, where it is not possible to alleviate cyst symptoms with only medication, the gynecologist may recommend surgery to remove the Skene gland.