Phototherapy consists of the use of special lights as a form of treatment, and is widely used in newborns born with jaundice, a yellowish tone in the skin, but which can also be useful for combating wrinkles and skin blemishes, as well as diseases such as psoriasis, vitiligo eczema, for example.
Phototherapy can also be used by physiotherapists to promote rejuvenation and combat small sun spots that can be caused by the sun. In the sessions, a special type of light is used, the Diode Emitted Light (LED) that stimulates or inhibits cellular activity.

Indications and contraindications
Phototherapy is indicated for the treatment of situations such as:
- Hyperbilirubinemia of the newborn;
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma;
- Psoriasis and parapsoriasis;
- Scleroderma;
- Lichen planus;
- Dandruff;
- Chronic eczema;
- Chronic urticaria;
- Purple:
- Rejuvenation and elimination of facial and hand patches.
To treat these and other diseases, the dermatologist can indicate 2 or 3 sessions per week. However, this technique should not be used during pregnancy or when increased bilirubin in the newborn is caused by kidney or liver problems in cases of porphyria, albinism, lupus erythematosus and pemphigus. People who have had cancer or close relatives such as parents, grandparents or siblings with cancer should also not have this type of treatment, as well as people who have used arsenic or have been exposed to ionizing radiation, and in case of cataracts or aphasia.
How it works
Phototherapy has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive action, and is useful for decreasing the overproduction of cells at specific sites of the skin. Sometimes to potentiate the effects of phototherapy the doctor may prescribe the use of medicines such as retinoids, methotrexate or cyclosporin before exposure to light.
During treatment, the person should remain with treated area exposed to light, protecting the eyes with a kind of slap eye that should be maintained throughout the treatment.
Phototherapy in newborns
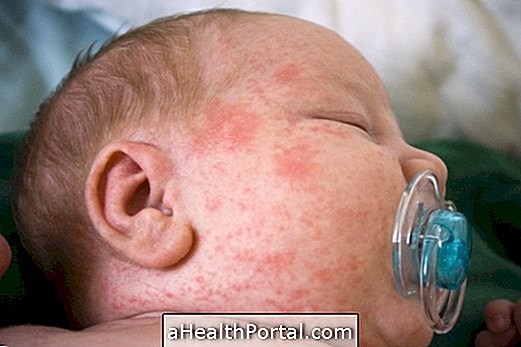
The baby born with hyperbilirubinemia usually has to stay in a special crib, doing phototherapy to eliminate excess bilirubin through the urine. The causes of this excess may be related to the use of medicines during pregnancy, such as diazepam, oxytocin during childbirth and also in the case of normal delivery with forceps or suction cup, or when there is intense bleeding.

The newborn is usually placed under a white or blue light, which can be placed 30 or 50 cm away from your skin, with your eyes properly covered with a specific sale, for the time determined by the pediatrician.
Phototherapy is especially indicated for babies born with very yellowish color because it prevents excess bilirubin from accumulating in the brain and can cause serious changes.
Can Phototherapy Cause Cancer?
Phototherapy should only be used under medical indication, complying with its recommendations regarding the number of sessions and time each of them for this is a safe method of treatment. Although not common, phototherapy can increase the risk of developing skin cancer, such as melanoma, when used for long periods, in susceptible people, such as those with cases of melanoma in the family.
Apparently the use of phototherapy for the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia and other skin changes does not cause cancer because this can never be proven in scientific research.